Press release
Lordfintube--Tubesheet for Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
Within the complex internal structure of a shell and tube heat exchanger, the tube sheet plays a pivotal role-it is not only the supporting skeleton for the tube bundle but also the critical barrier separating the tube-side and shell-side media. A well-designed and precisely manufactured tube sheet directly determines the efficiency, safety, and service life of the heat exchanger. As a professional manufacturer of heat exchanger tube sheets and baffles, we provide a comprehensive analysis of the core elements of tube sheet technology.1. What is a Tube Sheet? What Functions Does It Serve?
A tube sheet is a thick metal plate drilled with densely packed tube holes in a shell and tube heat exchanger. It is the core structural and pressure-bearing component. Its functions extend far beyond being a simple drilled plate, encompassing multiple critical roles:
Support and Fixation: Acting as the "skeleton" for hundreds or even thousands of heat exchanger tubes, it securely fixes the tube bundle in precise positions through expansion or welding processes, resisting vibration induced by fluid flow and ensuring long-term operational stability.
Pressure Boundary and Media Separation: It forms a rigid barrier between the tube-side (fluid inside tubes) and shell-side (fluid outside tubes/shell side) flows, strictly preventing the mixing of the two media. This is the core sealing interface ensuring process safety.
Bridge for Heat Transfer: The material and thickness design of the tube sheet directly affect the heat transfer path and efficiency from the tube side to the shell side (or vice versa). A rational tube sheet design can reduce thermal resistance.
Connection and Sealing: Connected via bolts to the heat exchanger shell flange and channel (header) flange, it forms a high-pressure sealing system with gaskets, withstanding pressure and temperature loads within the system.
In short, the tube sheet is a multifunctional key component integrating structural support, sealing isolation, and heat transfer conduction. Its design and manufacturing quality directly determine the performance and lifespan of the entire heat exchanger.
2. Tube Sheet Types
(1) Single Metal Tube Sheet
Manufactured entirely from a single material, this is the most traditional and economical form. Material choices range widely, from economical carbon steel to corrosion-resistant stainless steel, titanium, Hastelloy, etc. Its advantages are relatively simple manufacturing process, short lead time, and controllable cost. The disadvantage is that when facing highly corrosive media, using an entire plate of high-grade corrosion-resistant alloy can be very costly.
(2) Bimetallic Clad Tube Sheet
An efficient solution developed to resolve the conflict between corrosion resistance and cost. It uses a lower-cost base material (typically carbon steel) for structural strength and a thinner corrosion-resistant cladding material to resist media attack.
a. Overlay Welded (Clad) Tube Sheet
A layer (typically 3-10mm) of corrosion-resistant alloy is deposited onto the surface of a carbon steel or low-alloy steel base plate via processes like automatic submerged arc welding or strip cladding.
Process Characteristics: Metallurgical bond with high bonding strength; multi-layer overlay welding possible to achieve required thickness; post-weld heat treatment is required to relieve stress.
Application Scenarios: Suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature, heavy-duty equipment, especially where thicker cladding is needed or where field repair welding might be required.
b. Explosion-Bonded Clad Tube Sheet
Utilizes a precisely controlled explosive detonation to generate a high-pressure shockwave, causing two metals to collide at high velocity instantly, forming a solid-state metallurgical bond at the atomic level.
Process Characteristics: A cold-working process with no thermal effect on base material properties; the bonding interface is wavy, providing extremely strong mechanical bond; allows for combining metals with vastly different physical properties.
Diversity of Cladding Combinations:
Titanium-Steel Clad Plate: Cladding is commercial pure titanium (Gr.1, Gr.2) or titanium alloy. Widely used in seawater cooling, chlor-alkali industry, wet chlorine gas, and other chloride-ion-containing environments, offering excellent resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion.
Nickel-Steel Clad Plate: Cladding is pure nickel (Ni200/201) or Monel (Monel 400/500). Suitable for strong alkalis (e.g., NaOH), fluorine chemical industry, and reducing acid environments, offering excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Copper-Steel Clad Plate: Cladding is cupronickel (B10, B30) or naval brass. Primarily used in seawater condensers for ships and power stations, offering good thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance in seawater.
Stainless Steel-Steel Clad Plate: Cladding is 304, 316L, 2205 duplex steel, etc. This is the most common combination, suitable for corrosive environments in various industries like petrochemicals, food, and pharmaceuticals, offering good cost-effectiveness.
Application Scenarios: Highly corrosive media, where extremely high bonding strength between cladding and base is required, or where the two metals have poor weldability.
3. Tube Sheet Materials
(1) Forged Tube Sheet
Manufactured using forging processes, which improve the internal metal structure through forging, eliminate casting defects, and yield superior comprehensive mechanical properties and isotropy. This is the preferred choice for high-pressure, high-temperature, and high-hazard service conditions.
(Forged Tubesheet: https://www.lordfintube.com/high-pressure-forged-stainless-steel-tube-sheets_1463.html)
Common Forging Materials:
SA105: Carbon steel forging for non-corrosive media at ambient and elevated temperatures; a common material for pressure vessel flanges and tube sheets.
SA266 Gr.2/ Gr.4: Carbon and low-alloy steel forgings for pressure vessels. Gr.2 is carbon steel; Gr.4 is carbon-manganese steel with higher strength, suitable for moderate pressure/temperature conditions.
SA350 LF2: Carbon and low-alloy steel forging for low-temperature service, with good low-temperature impact toughness, commonly used in heat exchangers for low-temperature environments.
SA387 Gr.11/ Gr.22: Chromium-molybdenum alloy steel plate and forgings, offering excellent high-temperature strength and resistance to hydrogen attack. A standard material for hydrogen service (e.g., feed exchangers for hydrogenation reactors).
SA182 F304/F316/F321: Stainless and alloy steel forgings, corresponding to different stainless steel grades, used in corrosive environments. F321, containing titanium, offers enhanced resistance to intergranular corrosion.
(F304 Tubesheet: https://www.lordfintube.com/f304-tube-sheet_1320.html)
(2) Plate Tube Sheet
Made by directly cutting and machining from rolled steel plate. This offers good economy and short production cycles, suitable for medium-low pressure and non-extreme conditions.
Advantages: Low cost, fast delivery, stable and reliable performance from modern high-quality steel plate.
Materials: Commonly used pressure vessel plates like SA516 (carbon steel), SA240 304/316 (stainless steel), etc.
4. Connection Methods
(1) Fixed Tube Sheet
The tube sheets are welded and fixed to the shell, offering a simple structure, low manufacturing cost, and reliable sealing. However, special attention must be paid to thermal stress issues:
When the temperature difference between the tube side and shell side is significant (typically >50°C), the differential thermal expansion between the tube bundle and the shell generates substantial thermal stress.
Solutions: Install expansion joints, reduce shell wall thickness, or optimize operating temperatures.
Applicable Scenarios: Suitable for conditions with small temperature differences, low pressure, and clean shell-side media.
(Fixed Tubesheet: https://www.lordfintube.com/fixed-tubesheet_1393.html)
(2) Floating Tube Sheet
One tube sheet is fixed, while the other can float freely within the shell, effectively accommodating differential thermal expansion:
U-Tube Type: The tube bundle is U-shaped, with both ends fixed to the same tube sheet, allowing complete free expansion.
Packed Floating Head Type: The floating end uses packing for sealing, suitable for medium-to-low pressures and non-hazardous media.
Sliding Bearing Type: The floating tube sheet has a lug that slides inside the shell, requiring consideration of lubrication and wear.
Applicable Scenarios: Suitable for large temperature differences (>50°C) and when shell-side media are prone to fouling, necessitating bundle removal for cleaning.
(Floating Tubesheet: https://www.lordfintube.com/floating-tube-sheet_1525.html)
5. Tube Hole Layout on Tube Sheets
The arrangement of tube holes is the essence of tube sheet mechanical design, directly affecting heat transfer efficiency, pressure drop, vibration characteristics, and maintainability.
Four Primary Layout Patterns:
Triangular Pattern (30°): Tubes are arranged at a 30° angle on the tube sheet. This is the most compact arrangement, allowing the maximum number of tubes per unit area, offering the highest heat transfer efficiency and good shell-side turbulence. The drawback is that the flow channels between tubes are tortuous, making mechanical cleaning (rodding) difficult, often necessitating chemical cleaning.
(Triangular Tubesheet: https://www.lordfintube.com/triangular-tube-sheet_1416.html)
Rotated Triangular Pattern (60°): Tubes are arranged at a 60° angle, but each row is staggered by half a pitch. It inherits the compactness of the triangular pattern while providing some straight flow channels, facilitating mechanical cleaning. It is a balanced choice between the triangular and square patterns.
Square Pattern (90°): Tubes are arranged at a 90° angle on the tube sheet. This creates straight vertical and horizontal flow channels between tubes, offering the greatest ease for mechanical cleaning and inspection. The disadvantage is less compact tube layout, resulting in the fewest tubes within a given shell diameter and relatively lower heat transfer efficiency.
Rotated Square Pattern (45°): Tubes are arranged at a 45° angle. Compared to the square pattern, this increases fluid scouring at an angle, enhances turbulence, improves the heat transfer coefficient, while still maintaining relatively good straight channels for cleaning.
6. Tube Pass Arrangement on Tube Sheets
The number of tube passes refers to the number of times the tube-side fluid travels back and forth within the heat exchanger, achieved by machining pass partition grooves on the back of the tube sheet.
Common tube pass numbers include 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, etc.
Single Pass (1 Pass): Fluid enters from one channel (header), passes through all tubes once, and exits from the opposite channel. The simplest structure with the lowest pressure drop, suitable for high flow rate applications with modest temperature change requirements.
Two Pass (2 Pass): Fluid is divided into two streams within the channel by a partition. It flows through one half of the tubes, reverses direction in the opposite channel, and then flows through the other half. This is the most common multi-pass design, effectively increasing tube-side velocity and heat transfer coefficient.
Four Pass (4 Pass) and Above (6, 8, 10, 12 Pass): More complex pass partition arrangements cause the fluid to reverse direction multiple times within the tubes. The number of passes always appears in pairs (even numbers) to ensure the fluid inlet and outlet are on the same channel end, facilitating piping arrangement.
Selection Principle: Increasing the number of passes raises tube-side velocity and heat transfer coefficient, making the equipment more compact, but also significantly increases tube-side pressure drop, complicates the structure, and increases manufacturing cost.
Application Scenarios: Suitable for processes with relatively low flow rates but requiring large temperature changes, or to meet specific temperature cross requirements by using flow arrangements closer to counter-current (e.g., 4-pass shell side with 2-pass tube side).
Pass partition layout must strictly adhere to standards (e.g., TEMA) to ensure unobstructed flow in each pass and uniform flow distribution. The machining precision of the seal faces for the partition grooves must be extremely high to prevent inter-pass leakage (cross-flow).
7. Tube-to-Tube Sheet Joint Methods
This is a critical aspect of tube sheet manufacturing, directly determining the tube bundle's sealing integrity, pull-out strength, and fatigue resistance. The main methods are:
Strength Expansion (Mechanical/ Hydraulic): Utilizes mechanical, hydraulic, or explosive expansion force to plastically deform the tube and elastically deform the tube sheet hole, relying on the residual compressive force between them for sealing and pull-out resistance. Suitable for design pressures ≤4 MPa, design temperatures ≤300°C, with no severe vibration or significant stress corrosion cracking risk. Advantages: Mature process, no thermal stress induced. Disadvantages: Poor fatigue resistance, prone to relaxation at high temperatures.
Strength Welding: The tube sheet hole is grooved, the tube is inserted and welded to the tube sheet. This is the most commonly used method, especially suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature, vibrating, or gap corrosion-prone conditions. Advantages: High joint strength, reliable sealing. Disadvantages: Existence of weld heat-affected zone and residual stresses.
Expansion and Welding Combination: Combines the advantages of expansion and welding. Two common sequences:
Expand then Weld: Expansion eliminates the gap between tube and hole, improving weld fatigue resistance and preventing weld cracks.
Weld then Expand: Welding ensures strength, expansion relieves welding stresses and enhances sealing.
This is currently the preferred solution for high-end, severe service conditions (e.g., nuclear, large-scale petrochemical), offering high strength, high sealing integrity, and excellent fatigue and stress corrosion cracking resistance.
Internal Bore (Face) Welding: Welding is performed on the backside (channel side) of the tube-to-tube sheet joint. This method completely eliminates the crevice between the tube and tube hole, making it the ideal choice to prevent crevice corrosion and meet extremely high cleanliness requirements (e.g., food, nuclear industries). However, manufacturing cost and difficulty are also the highest.
8. Quality Control and Testing of Tube Sheets
To ensure long-term reliable operation of tube sheets under severe service conditions, a series of strict quality tests must be implemented. We follow international and domestic standards such as ASME and GB/T, performing the following key tests on each tube sheet:
(1) Dimensional and Geometric Tolerance Inspection
Tube Hole Diameter and Tolerance: 100% inspection of each tube hole using air gauges or precision plug gauges to ensure hole diameter tolerance (typically ±0.05~0.15mm) meets expansion or welding requirements.
Tube Hole Internal Surface Roughness: Sampling inspection of the tube hole inner wall to ensure Ra value meets process requirements (e.g., expansion may require Ra ≤12.5μm, welding may require smoother finish).
Overall Dimensions: Inspection of key dimensions like tube sheet outer diameter, thickness, tube layout circle diameter.
Sealing Surface Quality: Inspection of flange sealing surface flatness, parallelism, and surface roughness (typically Ra ≤3.2μm), ensuring no scratches or defects.
(2) Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
This is the core method for assessing the internal and surface quality of tube sheets. The testing focus differs for solid metal and clad tube sheets.
Single Metal Tube Sheet:
Ultrasonic Testing (UT): Detects internal defects like laminations, porosity, cracks in the plate or forging.
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) / Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT): Detects surface and near-surface cracks (MT for ferromagnetic materials, PT for non-ferromagnetic).
Bimetallic Clad Tube Sheet (Key Differences):
Bond Integrity Testing (UT): This is a mandatory test for clad plates. 100% scanning of the entire bonding interface using ultrasonic flaw detectors to ensure the metallurgical bond rate between base and cladding meets standard requirements (typically ≥99% or higher). Unbonded areas must be evaluated and repaired per standard.
Cladding Thickness Measurement: Ensures the corrosion-resistant layer thickness is uniform and not less than the specified minimum.
Surface Testing: PT on the cladding surface to ensure no cracks, porosity, or other defects.
(3) Chemical Composition Analysis
Melt Analysis: Sampling and analysis during material melting to obtain the original heat/heat lot composition report, serving as the basis for material acceptance.
Product Analysis: Verification analysis performed on samples taken from the finished tube sheet (or test coupon) to confirm the finished material's chemical composition meets standard requirements, especially for key alloying elements affecting corrosion resistance (e.g., Cr, Ni, Mo).
(4) Mechanical Properties Testing
Tensile Test: Samples taken from a prolongation of the tube sheet or from a test plate of the same heat/lot are subjected to tensile testing at room temperature and design temperature to determine yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation, verifying material strength meets design requirements.
(5) Visual Inspection
All surfaces of the tube sheet are inspected visually or with aids to ensure:
No harmful defects like cracks, folds, or slag inclusions.
Sealing surfaces are free from dents, scratches, or corrosion.
Tube hole edges are smooth, free from burrs or rolled edges.
Markings (e.g., material grade, heat number, flow direction) are clear, accurate, and permanent.
If you are interested in tube sheets or would like more information, please contact us.
Company Name: Shanghai T.S. Industrial Co. Ltd
Contact Name: Miss Estela
Contact Number: 0086-021-66030009
Address: No.2, Lane 1588 Youyi Road, Baoshan, Shanghai, The P. R. of China. Post. 201999
Email: estela@lordfintube.com
Website: https://www.lordfintube.com/
Shanghai T.S. Industrial Co., Ltd is a leading company specializing in the production of finned tubes, tube sheet, U bend tubes, and helical coiled pipe used in heat exchangers, boiler economizers, coolers, and heaters. Our focus is on supplying custom fin tubes, finned pipes, and tube sheets in various material configurations to enhance heat transfer rates and reduce operating costs. With our advanced production capabilities and commitment to quality, we deliver innovative and efficient solutions tailored to meet the specific needs of our clients in the heat exchanger and boiler industries.
This release was published on openPR.
Permanent link to this press release:
Copy
Please set a link in the press area of your homepage to this press release on openPR. openPR disclaims liability for any content contained in this release.
You can edit or delete your press release Lordfintube--Tubesheet for Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger here
News-ID: 4320394 • Views: …
More Releases from Shanghai T.S. Industrial Co.,Ltd
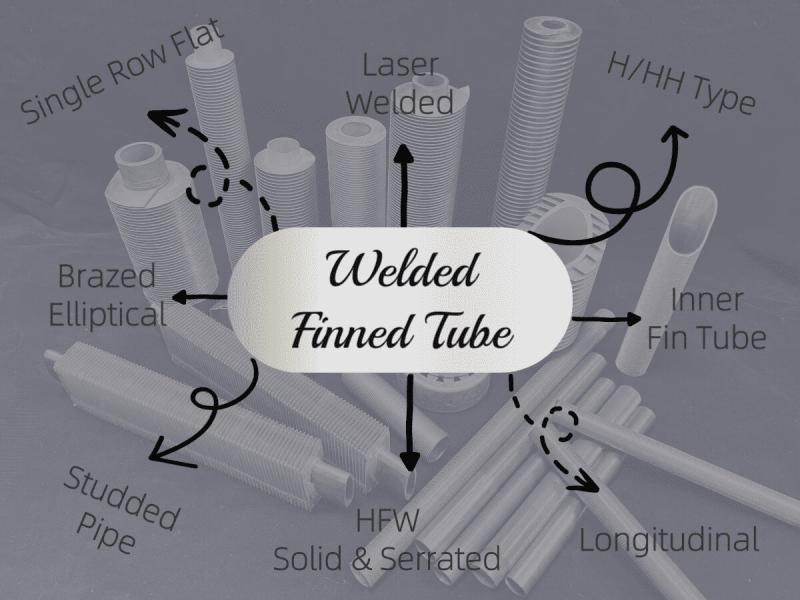
Eight Main Types of Welded Finned Tubes
In the field of industrial heat exchange, finned tubes, as a highly efficient heat transfer enhancement element, are widely used in equipment such as boilers, heat exchangers, and air coolers. Among the various methods of connecting fins to the base tube, welding processes have become the preferred solution in many scenarios due to their high bonding strength, low thermal resistance, and wide applicability to diverse operating conditions.
After in-depth research, there…
Do you know the most cost-efficiency bimetallic finned tube?
As a key heat transfer element, the finned tube's core function lies in balancing the difference in heat transfer coefficients between the two fluid sides of a heat exchanger. By installing fins on the side with a lower heat transfer coefficient, the heat transfer area is enlarged. It is indispensable in applications requiring enhanced heat transfer, such as boiler economizers and air coolers.
In industrial sectors like power, chemical, petrochemical, air…

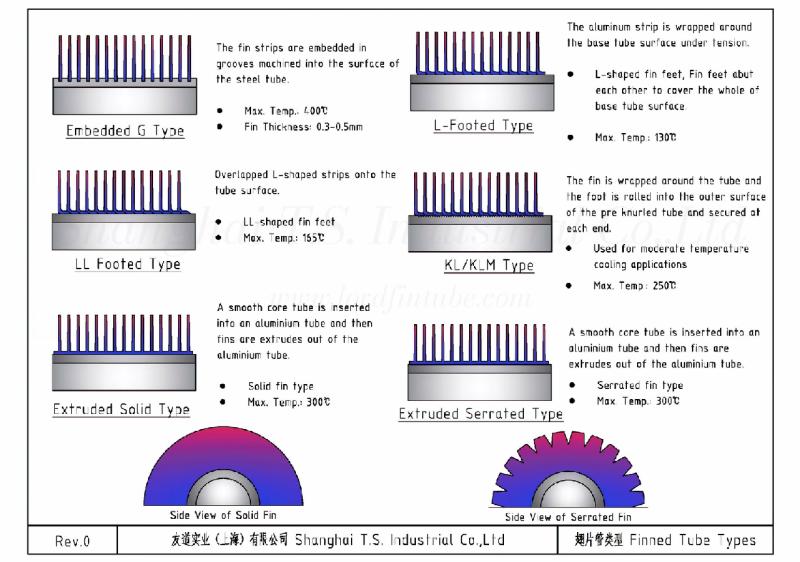
What's the Difference between L/LL/KL Type Finned Tube?
In an era where energy efficiency is increasingly vital to industrial operations, even minor performance improvements in heat exchangers-the core equipment for thermal energy recovery and management-can translate into significant operational cost savings. At the heart of most heat exchangers lies the finned tube, whose type selection directly dictates the entire system's efficiency, service life, and reliability. This article provides an in-depth analysis of three widely used finned tube types:…
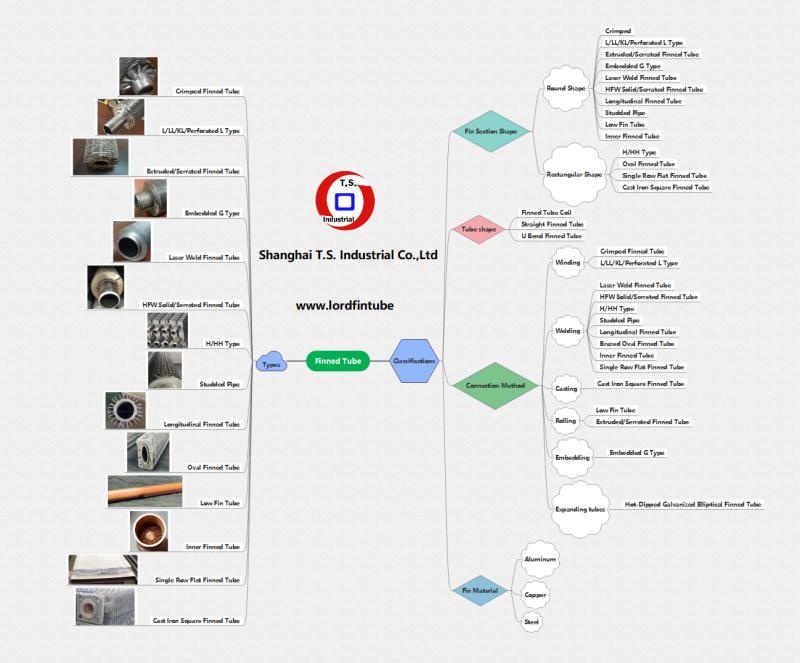
A Comprehensive Guide to Finned Tube Types |Heat Exchanger
Finned tubes are indispensable core components within heat exchangers across various sectors, including power engineering, chemical production, petroleum refining, air conditioning engineering, and refrigeration. By adding different types of fins to the internal or external surface of a base bare tube, the heat transfer area is significantly increased, leading to a substantial enhancement in heat exchange efficiency. Particularly in gas-liquid heat exchange scenarios, finned tubes effectively balance the difference in…
More Releases for Tube
Gastrostomy Feeding Tube (G-tube) Market Size, Share, Research Report 2026
LP information released the report titled "Global Gastrostomy Feeding Tube (G-tube) Market Growth 2026-2032" This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the global Gastrostomy Feeding Tube (G-tube) landscape, with a focus on key trends related to product segmentation, Gastrostomy Feeding Tube (G-tube) top 10 manufacturers' revenue and market share, Gastrostomy Feeding Tube (G-tube) report also provides insights into the strategies of the world's leading companies, focusing on their market share,…
Tube Swaging Service Market Size 2025, Trends, and Insights, Growth Forecast to …
NEW YORK, (UNITED STATES) - The global Tube Swaging Service Market has emerged as a pivotal sector, driving innovation and economic growth across industries. This in-depth market analysis delves into the evolving landscape of the Tube Swaging Service industry, highlighting key trends, growth drivers, challenges, and opportunities shaping its future. The report provides a holistic view of market dynamics, competitive strategies, and regional insights, offering stakeholders a comprehensive understanding of…
Large Honing Tube/Cylinder Tube/Hydraulic Steel Tube
Honed tube [https://www.jinyoindustry.com/] is usually a CDS (Cold drawn seamless) steel tube or DOM (Drawn Over Mandrel) steel tube with inside diameter honed or skived &roller burnished, so honed tubing is with extremely precise ID dimensions and smoothly ID surface.
Honed tubes are broadly utilized to produce and repair hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders. So in many fields, the honed tube is called cylinder tube also.
Honed tube usually is produced by…
Tube Packaging Market: Tube Packaging Market Developments: Shaping the Future of …
Market Overview:
Tube packaging refers to lightweight, flexible packaging solutions that are used for containing and transporting a variety of products like pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, dental products, and food. Tube packaging provides products protection, tampering evidence, and product shelf life extension.
Get Sample Report with Global Industry Analysis @ https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/insight/request-sample/571
Major Players Are:
✤ Albea S.A.
✤ Amcor Limited
✤ Essel Propack Limited
✤ Sonoco Products Company
✤ World Wide Packaging Inc.
✤ Montebello Packaging Inc.
✤ VisiPak Inc.
✤ Intrapac International…
Carbon steel seamless tube vs Stainless steel seamless tube
The difference between carbon steel seamless tube and stainless steel seamless tube mainly refers to the difference in design rules between carbon steel and stainless steel, which means that the design rules of these two types of steel cannot be used in common. These differences are summarized as follows:
Carbon steel
1. Ordinary steel is carbon steel, that is, iron-carbon alloy. According to the level of carbon content, it is divided into…
Tube-in-tube Sterilizer Market Growth 2020-2025
Global Tube-in-tube Sterilizer�Market Overview:
The latest report on the global Tube-in-tube Sterilizer�market�suggests a positive growth rate in the coming years. Analysts have studied the historical data and compared it with the current market scenario to determine the trajectory this market will take in the coming years. The investigative approach taken to understand the various aspects of the market is aimed at giving the readers a holistic view of the global Tube-in-tube…
