Press release
Urea Production Plant Cost 2026: Comprehensive Project Report and Market Outlook
The global urea production industry stands as a critical pillar of agricultural infrastructure and food security systems worldwide, positioned at the intersection of nitrogen fertilizer manufacturing, crop yield optimization, and global nutritional supply chains. As the most widely used synthetic nitrogen fertilizer globally, urea provides concentrated nutrient delivery supporting agricultural productivity across diverse crops, climates, and farming systems. This comprehensive guide provides an authoritative exploration of the technical, financial, and strategic dimensions of establishing a urea production plant, leveraging current market intelligence and industry insights to support informed investment decision-making in this strategically vital and economically significant agricultural chemicals manufacturing sector.Market Overview and Growth Potential
The urea production sector is experiencing steady growth driven by powerful, interconnected market forces that reflect fundamental transformations in global agricultural practices, food demand pressures, and government policy support for agricultural productivity enhancement. The industry's expansion is propelled by several critical factors:
• Rise in worldwide nitrogen fertilizer demand supporting crop production
• Larger area under agricultural cultivation globally
• Government incentives for farmers promoting crop yield optimization
• Increasing adoption of high-efficiency fertilizers
• Population growth driving food security imperatives
• Advancement of modern farming practices requiring balanced nutrition
The global urea market was valued at USD 53.49 Billion in 2025, establishing a substantial foundation reflecting the sector's central importance to global agricultural systems. According to comprehensive market analysis, the industry is projected to reach USD 61.16 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 1.5% during 2026-2034. While this growth rate reflects market maturity, the absolute market size demonstrates urea's indispensable role in agricultural systems, with steady expansion driven by continuous agricultural intensification and productivity improvement requirements worldwide.
The market expansion is fundamentally driven by increasing global food production demands and agricultural modernization trends. Urea consumption has significantly increased in Asia, Africa, and Latin America due to rising food demand, government subsidy programs supporting agricultural inputs, and growing awareness of balanced fertilization practices gaining public recognition. However, challenges remain in farmer education and agricultural extension services.
According to an Indian government Comptroller & Auditor General (CAG) audit for FY2022 surveying farmers in Madhya Pradesh, about 83% of farmers received no guidance from the agriculture department while 91% lacked training or seminars on proper fertilizer use. This knowledge gap paradoxically supports rising urea demand as farmers increasingly rely on it to boost crop yields, though it also highlights opportunities for improved agricultural extension services promoting balanced fertilization practices optimizing urea application efficiency.
The production of granulated and coated urea has enhanced application efficiency and reduced nitrogen losses through controlled-release technologies and improved physical properties, promoting market development through performance-enhanced products. Farmers in remote areas have gained improved access to urea through well-organized fertilizer distribution networks and emerging e-commerce platforms expanding market reach beyond traditional distribution channels.
IMARC Group's report, "Urea Production Plant Project Report 2026: Industry Trends, Plant Setup, Machinery, Raw Materials, Investment Opportunities, Cost and Revenue," offers a comprehensive guide for establishing a plant. The urea production plant cost report offers insights into the process, financials, capital investment, expenses, ROI, and more for informed business decisions.
Plant Capacity and Production Scale
A urea production plant operates as a sophisticated chemical manufacturing facility synthesizing urea (carbamide, CO(NH2)2) from ammonia and carbon dioxide through high-pressure chemical reactions. The production methodology represents a technically complex operation involving ammonia synthesis from natural gas, carbon dioxide recovery, high-pressure urea synthesis, product purification, and physical formulation into prilled or granular products meeting agricultural application requirements.
The proposed production facility is designed with an annual production capacity ranging between 500,000 - 1,000,000 MT (metric tons), representing world-scale production enabling substantial economies of scale while maintaining operational flexibility to accommodate product variations including standard prilled urea, granular formulations, and specialty coated products meeting specific agricultural application needs.
The facility produces urea for multiple application categories and end-use sectors:
• Agriculture sector: Primary application as nitrogen fertilizer for cereals (wheat, rice, corn), pulses, vegetables, and diverse field crops requiring nitrogen supplementation
• Fertigation and blending units: Precise nutrient application through irrigation systems and custom fertilizer blends formulated for specific crop requirements
• Horticulture and cash crops: Supporting high-value crop production including fruits, flowers, plantation crops, and specialty agricultural products demanding intensive nutrient management
• Industrial nitrogen source: Chemical feedstock for melamine manufacturing, urea-formaldehyde resin production, and various industrial chemical applications
• Animal feed additive: Non-protein nitrogen source in ruminant animal nutrition (cattle, sheep)
Production capacity planning must account for seasonal agricultural demand patterns reflecting planting and growing seasons requiring surge capacity, multiple product formulations including prilled, granular, and coated variations, stringent quality specifications ensuring nitrogen content (typically 46% minimum) and physical properties (particle size distribution, crushing strength, moisture content), integration with ammonia production or secure ammonia supply arrangements, and carbon dioxide sourcing typically from ammonia plant operations or industrial sources.
Request for a Sample Report: https://www.imarcgroup.com/urea-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
Financial Viability and Profitability Analysis
The urea production business presents compelling financial characteristics rooted in the transformation of natural gas and industrial chemicals into value-added agricultural nutrients supporting global food production systems. The project demonstrates healthy profitability potential under normal operating conditions, with gross profit margins typically ranging between 20-30% and net profit margins of 8-12%, supported by stable agricultural demand, government policy support, and essential role in crop production systems.
The financial projections developed for this project incorporate comprehensive analysis of capital investment requirements across land acquisition near natural gas sources or pipelines (natural gas representing both feedstock and fuel), specialized facility construction meeting chemical plant safety and environmental regulations, significant equipment procurement including ammonia synthesis units (if integrated), high-pressure urea reactors, CO2 compression systems, prilling or granulation towers, and product handling systems, utilities infrastructure supporting substantial steam, power, and cooling water requirements, and working capital for raw material inventory and finished product storage supporting seasonal agricultural demand patterns.
Operating cost modeling addresses raw material expenses dominated by natural gas procurement (serving both as feedstock for ammonia synthesis and fuel for process heating), typically representing 70-80% of operating costs and constituting the single largest cost component requiring strategic gas supply contracts and price risk management. Ammonia (if not produced on-site) represents the next critical raw material, with procurement strategies emphasizing reliability and quality specifications. Carbon dioxide, typically recovered from ammonia production processes or sourced from industrial operations, provides the second chemical feedstock for urea synthesis.
Utilities constitute 10-15% of operating expenses, with electricity consumption for compression systems, cooling water for process operations and product cooling, steam for various process heating applications, and process water for synthesis reactions and product washing representing substantial ongoing costs inherent to chemical manufacturing operations requiring significant energy inputs.
Additional operating costs encompass labor expenses for chemical plant operators managing complex continuous processes, maintenance technicians servicing high-pressure equipment, quality control analysts ensuring product specifications, and engineering staff supporting process optimization, maintenance of sophisticated chemical process equipment including high-pressure vessels, compressors, and materials handling systems requiring continuous upkeep, quality control costs including laboratory testing equipment and analytical reagents, environmental compliance addressing ammonia emissions, wastewater treatment, and greenhouse gas management, safety systems and training addressing chemical plant hazards, and packaging materials for bulk or bagged product distribution.
These detailed financial models provide stakeholders with transparent visibility into project economics, including comprehensive capital expenditure (CapEx) breakdowns particularly addressing substantial chemical process equipment investments, operating expenditure (OpEx) structures with critical emphasis on natural gas procurement strategies given dominant cost position and price volatility, income projections across agricultural seasons and regional markets, expected return on investment (ROI), net present value (NPV) calculations, payback period analysis typically ranging 5-7 years depending on capacity and market conditions, and long-term profitability trajectories under various natural gas pricing, agricultural demand, and government subsidy policy scenarios.
Operating Cost Structure
Understanding the operating cost structure is fundamental to effective business planning and margin management in urea production. The cost architecture reflects natural gas intensity, substantial energy requirements for chemical synthesis, and the capital-intensive nature of operations.
Key Raw Materials Include:
• Natural gas: Primary feedstock for ammonia synthesis (through steam reforming) and fuel for process heating, representing 70-80% of operating costs and the dominant economic factor
• Ammonia (NH3): If not produced on-site, purchased ammonia serves as primary nitrogen source for urea synthesis
• Carbon dioxide (CO2): Second chemical feedstock for urea synthesis, typically recovered from ammonia production off-gas or sourced from industrial operations
• Process chemicals: Catalysts for ammonia synthesis, inhibitors preventing corrosion, and additives for specialty products
Utilities and Process Requirements:
Substantial utility consumption reflects the energy-intensive nature of chemical synthesis and compression operations, covering electricity for gas compression, CO2 compression, product handling systems, and cooling equipment, steam for process heating in various unit operations, cooling water for exothermic reaction heat removal and product cooling (urea synthesis is highly exothermic), and process water for synthesis reactions, product washing, and utility systems.
Additional operating costs encompass:
• Transportation: Bulk urea distribution to agricultural markets, fertilizer blending facilities, and regional warehouses using specialized bulk carriers, rail cars, or bagged product trucking
• Packaging: Substantial costs for bagged product (typically 50 kg bags) including woven polypropylene bags, printing, and bagging equipment operations, with bulk shipments reducing packaging expenses
• Salaries and wages: Chemical plant operators managing continuous 24/7 operations, process engineers optimizing synthesis conditions, maintenance technicians servicing complex equipment, quality control analysts ensuring specifications, and safety personnel
• Depreciation: On substantial capital investments in chemical process equipment, high-pressure vessels, compression systems, and product formulation facilities
• Quality control: Laboratory equipment for nitrogen content analysis, moisture determination, particle size measurement, and physical property testing
• Environmental compliance: Ammonia emission control systems, wastewater treatment, greenhouse gas monitoring and reporting
• Safety systems: Gas detection systems, emergency shutdown systems, personal protective equipment, and comprehensive safety training programs
• Insurance: Premiums addressing chemical plant risks, business interruption, and product liability
Raw material procurement strategies represent the most critical success factor given natural gas's dominant cost position (70-80% of OpEx) and price volatility significantly impacting profitability. Strategic considerations include establishing long-term natural gas supply contracts with pricing mechanisms balancing fixed and variable components, implementing hedging strategies through futures markets or financial instruments managing price risk, optimizing energy efficiency reducing specific gas consumption per ton urea produced, exploring integration opportunities with ammonia production maximizing energy efficiency and reducing costs, and evaluating alternative feedstocks or emerging technologies (renewable hydrogen, carbon capture) supporting long-term sustainability and cost competitiveness.
Capital Investment Requirements
Establishing a urea production plant requires substantial capital investment reflecting the chemical process complexity, high-pressure equipment requirements, and safety systems essential for petrochemical manufacturing.
Capital Expenditure Components:
• Land and Site Development Costs: Significant land acquisition near natural gas pipeline infrastructure or petrochemical complexes, with adequate buffer zones meeting safety setback requirements for chemical facilities
• Civil Works Costs: Specialized chemical plant construction including high-pressure equipment foundations, process buildings, utilities infrastructure, control rooms, laboratories, and safety systems
• Machinery Costs: Largest portion of CapEx representing sophisticated chemical process technology
• Other Capital Costs: Safety systems, environmental equipment, initial catalyst inventory, regulatory permits, startup expenses
Site Selection Considerations:
Strategic location selection must evaluate several critical factors:
• Easy access to key raw materials particularly natural gas from pipelines or LNG terminals (dominant feedstock and fuel), ammonia supply (if not integrated), and carbon dioxide sources, minimizing feedstock transportation costs and ensuring supply reliability
• Proximity to target markets particularly major agricultural regions, fertilizer distribution networks, and port facilities for export markets, minimizing finished product transportation costs given bulk commodity nature
• Robust infrastructure including natural gas pipeline connections (critical infrastructure requirement), reliable electrical grid for substantial power consumption, cooling water sources (rivers, sea water), and transportation networks (rail, road, port access)
• Compliance with local zoning laws and environmental regulations governing chemical manufacturing facilities, particularly addressing air emissions, wastewater discharge, and safety setbacks from populated areas
• Labor availability supporting continuous chemical plant operations requiring shift workers, maintenance specialists, chemical engineers, and safety professionals
• Space for future expansion accommodating capacity increases or downstream product development (specialty fertilizers, industrial chemicals)
Essential Machinery Requirements:
High-quality, specialized chemical process equipment represents the technical foundation:
• Ammonia reactors: If integrated ammonia production, synthesis reactors operating at high temperature and pressure with catalyst beds converting natural gas-derived synthesis gas to ammonia
• Urea converters: High-pressure reactors where ammonia and carbon dioxide react forming ammonium carbamate and subsequently urea
• Prilling towers or granulators: Tall towers where molten urea is sprayed forming spherical prills, or granulation equipment producing larger granular products with superior handling characteristics
• Dryers and coolers: Equipment removing residual moisture and cooling urea product to stable storage temperature preventing caking
• Screening units: Classification equipment separating product into specification size ranges, with oversized and undersized material recycled
• Automated packaging systems: Bagging equipment, conveyors, palletizers for packaged product, or bulk loading systems for direct truck/rail shipment
Supporting infrastructure includes comprehensive process control systems with distributed control systems (DCS) managing complex chemical processes, safety instrumented systems (SIS) providing multiple layers of protection, analytical equipment for continuous process monitoring, ammonia and carbon dioxide compression systems achieving reaction pressures, heat recovery systems capturing exothermic reaction heat for steam generation or process heating improving energy efficiency, wastewater treatment facilities managing process condensates and cooling water blowdown, air emission control systems including ammonia scrubbers and particulate control, and comprehensive safety systems including gas detection, fire suppression, and emergency response equipment.
Civil works costs encompass substantial chemical plant construction with reinforced concrete foundations supporting heavy high-pressure equipment, process buildings housing synthesis units with explosion-proof electrical systems, control rooms providing safe operator interface with hazardous processes, quality control laboratories with fume hoods and analytical instruments, maintenance workshops with specialized tools and spare parts storage, utilities including cooling towers, steam generation, and water treatment, storage facilities for finished urea with capacity supporting seasonal demand patterns, and comprehensive safety infrastructure. Other capital costs include sophisticated safety systems, environmental permits and impact assessments, initial catalyst and chemical inventory, commissioning and startup expenses, operator training programs, and contingency reserves addressing construction or equipment procurement uncertainties.
Ask Analyst for Customization: https://www.imarcgroup.com/request?type=report&id=7647&flag=C
Manufacturing Process Overview
The urea production process involves sophisticated sequential chemical operations designed to synthesize urea from basic chemical feedstocks through controlled high-pressure reactions:
Unit Operations Involved:
• Ammonia synthesis: (If integrated) Natural gas steam reforming producing hydrogen-rich synthesis gas, followed by catalytic synthesis converting nitrogen and hydrogen to ammonia under high pressure and temperature
• Carbon dioxide recovery: CO2 separation from ammonia plant off-gas or other industrial sources, compression to reaction pressure
• Carbamate formation: Ammonia and carbon dioxide reaction at high pressure forming ammonium carbamate intermediate
• Urea synthesis: Ammonium carbamate dehydration forming urea and water under elevated temperature and pressure
• Decomposition and purification: Unreacted carbamate decomposition, ammonia and CO2 recovery and recycle, urea solution concentration
• Prilling or granulation: Molten urea formulation into solid product through spray prilling or granulation processes
• Drying and cooling: Moisture removal and temperature reduction to stable storage conditions
• Screening and packaging: Size classification, quality inspection, bagging or bulk loading for distribution
Quality Assurance Criteria:
Comprehensive quality control systems must monitor raw material purity ensuring ammonia and CO2 specifications, process parameters throughout high-pressure synthesis operations optimizing conversion and minimizing byproducts, product composition verifying nitrogen content, moisture content, biuret content, and physical properties including particle size distribution, crushing strength, and caking tendency critical for handling and agricultural application effectiveness.
Technical Tests:
Laboratory analysis includes nitrogen content determination through Kjeldahl method or combustion analysis, moisture content measurement critical for storage stability, biuret analysis ensuring low levels of this urea polymerization product potentially toxic to seedlings, particle size distribution measurement for application equipment compatibility, crushing strength testing ensuring mechanical durability during handling, and caking tendency evaluation under controlled humidity conditions.
Major Applications and Market Segments
Urea production serves multiple essential applications across diverse agricultural and industrial categories:
Primary Applications:
• Soil nitrogen enrichment: Direct application to agricultural soils providing readily available nitrogen supporting crop growth and protein synthesis
• Crop production: Cereal crops (wheat, rice, corn), pulses, vegetables, oilseeds, and diverse field crops requiring nitrogen fertilization
• Fertilizer blending: Component in NPK (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) blends and custom formulations meeting specific crop and soil requirements
• Hydroponics: Nitrogen source in soilless cultivation systems for vegetables and specialty crops
• Industrial chemical manufacture: Feedstock for melamine production, urea-formaldehyde resins, and various nitrogen-containing chemicals
End-Use Industries:
• Agriculture: Primary sector consuming of global urea production for crop nutrition
• Horticulture: Intensive cultivation systems for high-value crops including fruits, flowers, and vegetables
• Animal feed: Non-protein nitrogen supplement in ruminant nutrition (cattle, sheep, goats)
• Chemical manufacturing: Industrial applications including resins, adhesives, and specialty chemicals
• Fertilizer blending: Facilities producing customized fertilizer formulations for specific agricultural applications
The diversity of applications creates multiple revenue opportunities, though agricultural fertilizer applications dominate production volumes and market dynamics, with industrial applications providing higher-margin specialty segments.
Why Invest in Urea Production?
Multiple strategic factors converge to make urea production an exceptionally attractive investment proposition:
✓ Rising Agricultural Demand: Expanding global population and food demand drive nitrogen fertilizer markets, with urea representing the most concentrated and economically efficient nitrogen source supporting crop productivity worldwide.
✓ Consistency and Efficiency: Centralized industrial production ensures standardized plant nutrients and dependable crop productivity supporting modern agricultural systems requiring reliable input quality.
✓ Government Support: Large-scale fertilizer production and distribution receive government subsidies, favorable policies, and infrastructure support in major agricultural nations recognizing fertilizer's strategic importance for food security.
✓ Product Customization Opportunities: Different urea types including prilled, granular, coated, and slow-release formulations offer application flexibility based on specific crops, soils, and farming systems, supporting market segmentation and margin optimization.
✓ Scalable and Cost-Efficient Production: World-scale production with state-of-the-art technology guarantees cost competitiveness through economies of scale and efficient resource utilization.
✓ Essential to Food Security: Urea's critical role in global agricultural productivity makes it strategically important infrastructure supporting national and global food security objectives.
✓ Established Market Infrastructure: Well-developed distribution networks, government procurement systems, and agricultural extension services support market access and demand stability.
✓ Technology Advancement Opportunities: Continuous innovation in energy efficiency, emissions reduction, and product enhancement creates opportunities for competitive advantage through operational excellence.
✓ Multiple Revenue Streams: Agricultural fertilizer sales combined with industrial chemical applications and potential carbon credit opportunities (with carbon capture integration) enhance overall project economics.
Industry Leadership
The global urea production industry features several established leaders with extensive manufacturing capacities:
Leading Urea Producers:
• CF Industries Holdings Inc
• CJ Chemicals
• Dakota Gasification Company
• Koch Fertilizer LLC
• Yara North America Inc
These major producers operate large-scale facilities serving end-use sectors including agriculture, horticulture, fertilizer blending, and industrial nitrogen applications across global markets. Their market presence demonstrates the scalability and profitability potential of professional urea production operations supporting diverse agricultural and industrial applications.
Latest Industry Developments
The urea sector continues to experience significant capacity expansion and strategic investment:
• December 2025: The Indian government laid foundation stone of the Ammonia-Urea Fertilizer Project of Assam Valley Fertilizer and Chemical Company Limited at Namrup in Dibrugarh, Assam. The project involves approximately INR 11,000 crore investment to build new plant with annual production exceeding 12 lakh metric tons (1.2 million MT), which government projects will improve urea supply, reduce logistics costs, and generate employment in Northeast India.
• November 2025: Mitsubishi commenced construction of major USD 1.3 billion urea production facility in Kiyanly on Caspian Sea coast in Turkmenistan, marking one of the largest fertilizer projects in the region. The new plant is expected to produce 3,500 tons of urea and 2,000 tons of ammonia per day once completed between 2028 and 2029, aligning with Turkmenistan's strategic goal to diversify chemical manufacturing base beyond natural gas exports.
These developments underscore industry trends toward world-scale capacity expansion leveraging natural gas resources, strategic geographic diversification into gas-rich regions, substantial capital investment (USD 1.3 billion, INR 11,000 crore projects) reflecting capital-intensive nature, government support recognizing fertilizer's strategic importance for agricultural development and employment generation, and integration of ammonia and urea production maximizing efficiency and cost competitiveness.
Buy Now: https://www.imarcgroup.com/checkout?id=7647&method=2175
Conclusion
The urea production sector presents an exceptionally compelling investment opportunity characterized by strong agricultural fundamentals, essential role in global food security, government policy support, and attractive profitability potential supported by efficient transformation of natural gas into concentrated nitrogen fertilizers.
For entrepreneurs and businesses seeking to participate in the essential agricultural infrastructure supporting global food security, crop productivity enhancement, and sustainable agricultural intensification, urea production offers a proven pathway to creating substantial value while contributing to critical food production systems, agricultural economic development, and nutritional security solutions. The sector's robust fundamentals, supported by agricultural demand growth, government policy backing, mature production technologies, and strategic importance for food security, combined with ongoing innovation in energy efficiency, emissions reduction, and product enhancement, ensure continued market relevance and attractive opportunities for well-planned and professionally executed manufacturing ventures delivering consistent quality, operational excellence, and cost competitiveness across diverse agricultural and industrial applications.
About Us:
IMARC Group is a global management consulting firm that helps the world's most ambitious changemakers to create a lasting impact. The company provide a comprehensive suite of market entry and expansion services. IMARC offerings include thorough market assessment, feasibility studies, company incorporation assistance, factory setup support, regulatory approvals and licensing navigation, branding, marketing and sales strategies, competitive landscape and benchmarking analyses, pricing and cost research, and procurement research.
Services:
• Plant Setup
• Factoring Auditing
• Regulatory Approvals, and Licensing
• Company Incorporation
• Incubation Services
• Recruitment Services
• Marketing and Sales
Contact Us:
IMARC Group
134 N 4th St. Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
Email: sales@imarcgroup.com
Tel No:(D) +91 120 433 0800
United States: +1-201971-6302
This release was published on openPR.
Permanent link to this press release:
Copy
Please set a link in the press area of your homepage to this press release on openPR. openPR disclaims liability for any content contained in this release.
You can edit or delete your press release Urea Production Plant Cost 2026: Comprehensive Project Report and Market Outlook here
News-ID: 4374702 • Views: …
More Releases from IMARC Group

Chocolate Manufacturing Plant Setup Cost Analysis (DPR) 2026: Complete Investmen …
The global chocolate manufacturing industry is witnessing robust growth driven by the rapidly expanding confectionery sector and increasing demand for premium and specialty chocolate products. At the heart of this expansion lies a beloved consumer product: chocolate. As consumer preferences transition toward artisanal varieties, organic ingredients, and innovative flavor combinations, establishing a chocolate manufacturing plant presents a strategically compelling business opportunity for entrepreneurs and food industry investors seeking to capitalize…

Saffron Processing Plant Cost (DPR) 2026: CapEx/OpEx Analysis with Profitability …
Saffron, widely recognized as the most expensive spice in the world, is derived from the dried red stigmas of the Crocus sativus flower. Renowned for its distinct aroma, vivid color, and exceptional culinary and medicinal properties, saffron has cemented its position as a high-value agricultural commodity with significant global demand. Each flower yields only three stigmas, requiring vast manual labor to harvest and process, which contributes to its premium market…

Irish Whiskey Market: Premium Spirit Positioning and Export-Led Consumption Mome …
Market Overview
The global Irish whiskey market was valued at USD 5.7 Billion in 2025 and is forecasted to reach USD 10.0 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 6.18% during the forecast period 2026-2034. The market growth is driven by rising premiumization trends, increasing demand for craft spirits, a growing cocktail culture, and strong off-trade sales. The industry also benefits from heritage-driven branding and expanding global consumer interest.
Study Assumption Years
• Base…
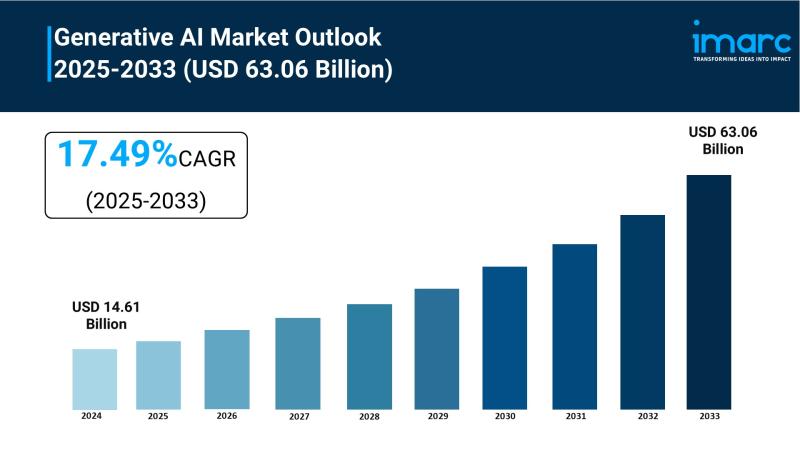
Generative AI Market to Reach USD 63.06 Billion by 2033, Growing at a CAGR of 17 …
Market Overview:
The generative AI market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by Surging Enterprise Adoption Across Industries, Cloud Infrastructure and API Accessibility and Government Funding and National AI Strategies. According to IMARC Group's latest research publication, "Generative AI Market : Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2025-2033" The global generative AI market size was valued at USD 14.61 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group estimates the market…
More Releases for Urea
Urea Formaldehyde Market Size Report 2025
"Global Urea Formaldehyde Market 2025 by Manufacturers, Regions, Type and Application, Forecast to 2031" is published by Global Info Research. It covers the key influencing factors of the Urea Formaldehyde market, including Urea Formaldehyde market share, price analysis, competitive landscape, market dynamics, consumer behavior, and technological impact, etc.At the same time, comprehensive data analysis is conducted by national and regional sales, corporate competition rankings, product types and applications. This report…
Global Marine Urea Solution Market Size by Application, Type, and Geography: For …
According to Market Research Intellect, the global Marine Urea Solution market under the Aerospace and Defense category is expected to register notable growth from 2025 to 2032. Key drivers such as advancing technologies, changing consumer behavior, and evolving market dynamics are poised to shape the trajectory of this market throughout the forecast period.
The market for marine urea solutions is expanding significantly due to stricter environmental rules that aim to lower…
Urea market: Market Indicators Showing Positive Outlook
The new report published by The Business Research Company, titled Urea Global Market Report 2024 - Market Size, Trends, And Global Forecast 2024-2033, delivers an in-depth analysis of the leading size and forecasts, investment opportunities, winning strategies, market drivers and trends, competitive landscape, and evolving market trends.
As per the report, the urea market size has grown steadily in recent years. It will grow from $47.64 billion in 2023…
Granular Urea Market: Cultivating Growth and Fertility with Premium Granular Ure …
The Worldwide "Granular Urea Market" 2023 Research Report presents a professional and complete analysis of the Global Granular Urea Market in the current situation. This report includes development plans and policies along with Granular Urea manufacturing processes and price structures. the reports 2023 research report offers an analytical view of the industry by studying different factors like Granular Urea Market growth, consumption volume, Size, revenue, share, trends, and Granular Urea…
Urea Market: Asia-Pacific to Lead Urea Market Growth with Rapid Industrializatio …
[100+ Pages Report] | Global "Urea Market" research report provides Innovative Insights on the Strategies adopted by Major Global in the worldwide industry. This valuable information offers businesses and investors a clear understanding of the market's Competitive Landscape, Growth Potential, and Impending Opportunities. The modern report highlights Latest Mergers, Achievements, Revenue Offshoring, R & D, Development Plans, Progression Growth, and Collaborations.
The global urea market size was valued at USD 107.28…
Polymer Sulphur Coated Urea Accounts for Over 90% of the Sales of Global Sulphur …
The impact of the COVID-19 outbreak has compelled several manufacturers and industries to rethink their operations to gradually recover from the losses incurred for years to come. The organic chemicals industry suffered a huge setback due to halted production and a limited supply of raw materials.
The report offers actionable and valuable market insights of Polymer Sulphur Coated Urea. The latest report by Fact.MR provides details on the present scenario of the…
