Press release
Cost of Setting Up a Second-Generation Ethanol Production Plant & DPR 2026
The global renewable energy and sustainable fuels industry is experiencing revolutionary transformation driven by decarbonization imperatives, transportation sector emission reduction requirements, and strategic shift from fossil fuels toward low-carbon alternatives. At the forefront of this advanced biofuels revolution stands second-generation ethanol (cellulosic ethanol) production-a breakthrough technology converting non-food lignocellulosic biomass into renewable transportation fuel. As governments worldwide mandate advanced biofuel targets, industries seek to decarbonize transport fuels, agricultural and forestry residues present low-cost feedstock opportunities, and investments accelerate in commercial-scale biorefineries and demonstration facilities, establishing a second-generation ethanol production plant presents a strategically compelling business opportunity for renewable energy investors, agricultural processors, chemical companies, and sustainability-focused entrepreneurs seeking to capitalize on the explosive market growth for advanced biofuels serving transportation, fuel distribution, chemical intermediates, and low-carbon fuel compliance applications across diverse industrial segments pursuing aggressive climate goals worldwide.IMARC Group's report, "Second-Generation Ethanol Production Plant Project Report 2026: Industry Trends, Plant Setup, Machinery, Raw Materials, Investment Opportunities, Cost and Revenue," offers a comprehensive guide for establishing a production plant. The second-generation ethanol production plant report offers insights into the production process, financials, capital investment, expenses, ROI, and more for informed business decisions.
Request for a Sample Report: https://www.imarcgroup.com/second-generation-ethanol-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
Market Overview and Explosive Growth Potential
The global second-generation ethanol market demonstrates exceptional growth trajectory, valued at USD 16.72 Billion in 2025. According to IMARC Group's comprehensive market analysis, the market is projected to reach USD 141.66 Billion by 2034, exhibiting an extraordinary CAGR of 26.8% from 2026-2034-representing one of the highest growth rates across all renewable energy technologies. This sustained explosive expansion is fueled by advanced biofuel mandates, need to decarbonize transport fuels, utilization of agricultural and forestry residues as low-cost feedstocks, and substantial investments in commercial-scale biorefineries and demonstration facilities.
Second-generation ethanol (2G/cellulosic ethanol) is bioethanol produced from non-food lignocellulosic biomass such as agricultural residues (corn stover, wheat straw, rice straw), sugarcane bagasse, forestry residues, and energy crops. Unlike first-generation ethanol derived from food crops, 2G ethanol converts cellulose and hemicellulose into fermentable sugars through pretreatment and hydrolysis, followed by fermentation and purification. Key attributes include potential for lower lifecycle greenhouse-gas emissions versus fossil gasoline and elimination of food-versus-fuel conflicts that have constrained conventional ethanol expansion.
Manufacturing performance depends heavily on pretreatment efficiency, enzyme use, inhibitor management, and fermentation of both C6 and C5 sugars. The global effort to lower greenhouse gas emissions and shift towards low-carbon, renewable transportation fuels is driving unprecedented policy support, with governments worldwide encouraging advanced biofuels development from non-food biomass to counter sustainability issues linked to first-generation ethanol.
Plant Capacity and Production Scale
The proposed second-generation ethanol production facility is designed with an annual production capacity ranging between 50,000-200,000 kiloliters (KL) per year, enabling economies of scale while maintaining operational flexibility. This capacity range allows manufacturers to serve diverse market segments-from transportation fuels and gasoline blending to oil and gas fuel distribution, chemical intermediates/industrial solvents, and sustainable fuels supply chains-ensuring steady demand and consistent revenue streams across multiple distribution channels serving the expanding renewable fuels market.
Buy Now: https://www.imarcgroup.com/checkout?id=28323&method=2175
Financial Viability and Profitability Analysis
The second-generation ethanol production business demonstrates healthy profitability potential under normal operating conditions. The financial projections reveal solid margins supported by policy mandates and premium pricing for advanced biofuels:
• Gross Profit Margins: 25-35%
• Net Profit Margins: 10-20%
These margins position second-generation ethanol production among mid-tier profitability ventures in the renewable energy sector. The project demonstrates attractive return on investment (ROI) potential, supported by residue-to-value pathway upgrading agricultural and forestry residues into transport fuel, policy-aligned decarbonization with advanced biofuel targets improving long-term offtake visibility, reduced food-crop dependence mitigating competition with food markets, platform for biorefinery co-products including power generation from lignin-rich residues, and technology and quality barriers favoring capable players with pretreatment know-how, enzyme/fermentation optimization, and stringent process control.
Operating Cost Structure
Understanding the operating expenditure (OpEx) is crucial for effective financial planning and cost management. The cost structure for a second-generation ethanol production plant reflects resource-intensive biorefinery operations:
• Raw Materials: 50-60% of total OpEx
• Utilities: 25-35% of OpEx
• Other Expenses: Including labor, packaging, transportation, maintenance, quality control, depreciation, and taxes
Lignocellulosic biomass (agricultural waste) constitutes the primary raw material cost driver at 50-60% of operating expenses, with enzymes for hydrolysis and yeast for fermentation representing additional significant inputs. The substantial utility costs (25-35%) reflect energy-intensive processes including pretreatment (mechanical, chemical, or steam-based), enzymatic hydrolysis requiring controlled conditions, fermentation operations, distillation and dehydration to fuel-grade specifications, and by-product recovery systems. This high utility component underscores the importance of integrated cogeneration systems utilizing lignin-rich residues for onsite power generation, substantially improving overall plant economics beyond ethanol production alone.
Capital Investment and Project Economics
Establishing a second-generation ethanol production plant requires comprehensive capital investment covering land acquisition, site preparation, civil works, specialized machinery procurement, and working capital. Machinery costs account for the largest portion of total capital expenditure, with essential equipment including feedstock processing machines (shredders, chippers), pretreatment reactor systems (mechanical, chemical, or steam explosion), enzymatic hydrolysis tanks maintaining optimal conditions for cellulose breakdown, bioreactors for fermentation of both C6 and C5 sugars, distillation units purifying ethanol, evaporators concentrating by-products, and solid-liquid separation equipment. All machinery must comply with industry standards for safety, efficiency, reliability, and environmental performance.
Operating costs in the first year are projected to be significant, covering raw materials (lignocellulosic biomass, enzymes, yeast), utilities (steam, electricity, water for extensive processing), depreciation, taxes, packaging, transportation, and repairs and maintenance. By the fifth year, total operational costs are expected to increase substantially due to inflation, market fluctuations, potential rises in enzyme and feedstock costs, supply chain dynamics, rising demand for advanced biofuels, and shifts in carbon pricing mechanisms driving overall cost escalation. However, technological learning curves and economies of scale typically improve production efficiency over time, partially offsetting cost increases.
Major Applications and End-Use Industries
Second-generation ethanol serves critical applications across renewable fuels ecosystem:
• Transportation Fuels and Fuel Blending: Used as renewable blending component reducing fossil gasoline consumption and supporting emissions reduction targets and renewable fuel mandates globally
• Oil and Gas Distribution/Fuel Marketing: Procured for compliance with renewable fuel obligations and supplied through terminals for blended fuel distribution networks
• Low-Carbon Fuel Programs and Credits: Integrated into LCFS-style frameworks generating compliance value based on pathway carbon intensity, with Canada's Clean Fuel Regulations leading to 6% biofuel consumption growth
• Industrial and Chemical Use: Used as solvent or intermediate input where specifications and commercial economics support non-fuel diversion (generally smaller than fuel demand)
Why Invest in Second-Generation Ethanol Production?
Several compelling factors make second-generation ethanol production an exceptional investment opportunity:
• Explosive Market Growth: 26.8% CAGR (2026-2034) driving market from USD 16.72 Billion to USD 141.66 Billion-one of highest growth rates in renewable energy sector
• Residue-to-Value Pathway: Upgrades agricultural and forestry residues into transport fuel, creating monetization route for low-value biomass while reducing open-field burning and residue disposal challenges
• Policy-Aligned Decarbonization: Advanced biofuel targets and feedstock eligibility lists improve long-term offtake visibility, encouraging investment in large, compliant biorefineries meeting sustainability and traceability requirements
• Reduced Food-Crop Dependence: Using lignocellulosic feedstocks mitigates direct competition with food starch/sugar markets, supporting energy transition without relying on edible raw materials
• Platform for Biorefinery Co-Products: Facilities integrate power generation from lignin-rich residues and explore additional co-products (technology-dependent), improving overall plant economics beyond ethanol alone
• Technology and Quality Barriers: Pretreatment know-how, enzyme/fermentation optimization, and stringent process control create higher entry barriers than conventional distilleries, favoring engineered, quality-focused manufacturing setups
• Energy Security Benefits: Rising concerns about energy security and fossil fuel price volatility boost appeal of locally produced cellulosic fuels
Manufacturing Process Overview
The second-generation ethanol production process involves several critical stages ensuring product quality and sustainability. Feedstock handling begins with biomass collection, storage, and preprocessing including size reduction, cleaning, and drying operations preparing materials for conversion. Pretreatment (mechanical, chemical, or steam-based) breaks lignocellulose structure, disrupting crystalline cellulose and separating components for subsequent processing.
Enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose and hemicellulose into fermentable sugars proceeds in controlled conditions optimizing enzyme activity and sugar yields. Fermentation operations convert sugars into ethanol using specialized microorganisms capable of metabolizing both C6 (glucose) and C5 (xylose, arabinose) sugars-a critical capability distinguishing 2G from conventional ethanol production. Distillation and dehydration concentrate ethanol to fuel-grade specifications meeting transportation fuel standards and blending requirements.
By-product recovery systems capture lignin-rich residues for cogeneration power production, biogas for process heat, and CO2 for potential carbon capture applications or industrial use. Quality control throughout production monitors ethanol concentration, purity, water content, and contamination ensuring regulatory compliance and customer specifications. The integrated biorefinery approach maximizing value from all biomass components substantially improves project economics beyond ethanol revenue alone.
Ask Analyst for Customization: https://www.imarcgroup.com/request?type=report&id=28323&flag=C
Industry Leadership and Key Players
The global second-generation ethanol industry features several innovative companies pioneering commercial-scale production. Leading producers include Novozymes A/S, Clariant AG, POET LLC, Beta Renewables S.p.A., LanzaTech Inc., and Abengoa S.A., all serving end-use sectors including transportation fuels, oil and gas fuel distributors, chemical intermediates/industrial solvents, and sustainable fuels supply chains. These industry leaders demonstrate the technological feasibility and scalability of cellulosic ethanol production serving global renewable fuels markets.
Recent Developments and Market Dynamics
Recent industry developments highlight accelerating commercial deployment and technological validation. In January 2026, LanzaTech Global was awarded a contract by Praj Engineering Devices Ltd. to build a second-generation ethanol facility in Uttar Pradesh, India, that will use sugarcane bagasse to produce sustainable second-generation ethanol. The plant is designed to process up to 300 tons of bagasse per day, generate nutrient-rich biochar for agriculture, and is expected to start operations within two years.
In June 2025, Toyota developed biomass-based bioethanol in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan, producing fuel from non-edible agricultural residues such as rice straw and forestry by-products to support lower-carbon transportation. The initiative aligns with broader efforts to reduce emissions from internal combustion engines and strengthen energy security through domestic renewable fuel production.
These developments demonstrate strong industry fundamentals with major corporations validating commercial viability, technology transfer accelerating global deployment particularly in agricultural regions with abundant residue availability, and government support through policy frameworks and infrastructure investments creating favorable market conditions for sustained growth.
Policy Support and Circular Economy Benefits
The use of agricultural residues, forestry residues, and energy crops helps meet circular economy goals while lowering open-field burning and waste disposal issues prevalent in many agricultural regions. Blending requirements and renewable fuel standards are encouraging fuel manufacturers to incorporate second-generation ethanol into gasoline supply chains globally. Canada's Clean Fuel Regulations leading to 6% growth in biofuel consumption, with preference for cleaner fuels, exemplifies the policy tailwinds supporting advanced biofuels adoption.
Government policies worldwide rendering low-carbon industrial operations financially attractive and supporting renewable energy use drive investments into second-generation ethanol production plants. Advanced biofuel mandates, feedstock eligibility lists, and carbon credit programs improve long-term offtake visibility, encouraging investment in large, compliant biorefineries meeting stringent sustainability and traceability requirements essential for policy compliance and market access.
About Us:
IMARC Group is a global management consulting firm that helps the world's most ambitious changemakers to create a lasting impact. The company excels in understanding its client's business priorities and delivering tailored solutions that drive meaningful outcomes. We provide a comprehensive suite of market entry and expansion services. Our offerings include thorough market assessment, feasibility studies, company incorporation assistance, factory setup support, regulatory approvals and licensing navigation, branding, marketing and sales strategies, competitive landscape, and benchmarking analyses, pricing and cost research, and procurement research.
Contact Us:
IMARC Group
134 N 4th St. Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
Email: sales@imarcgroup.com
Tel No: (D) +91 120 433 0800
United States: (+1-201-971-6302)
This release was published on openPR.
Permanent link to this press release:
Copy
Please set a link in the press area of your homepage to this press release on openPR. openPR disclaims liability for any content contained in this release.
You can edit or delete your press release Cost of Setting Up a Second-Generation Ethanol Production Plant & DPR 2026 here
News-ID: 4394103 • Views: …
More Releases from IMARC Group
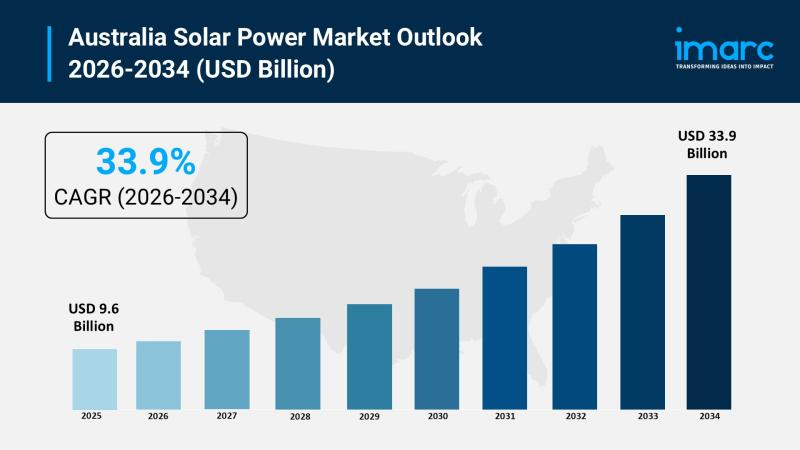
Australia Solar Power Market 2026 | Projected to Reach USD 33.9 Billion by 2034
Market Overview
The Australia solar power market reached USD 9.6 Billion in 2025 and is forecast to grow to USD 33.9 Billion by 2034. The market exhibits a robust growth rate of 15.00% during the forecast period 2026-2034. This expansion is driven by supportive government policies, technological advancements, and increasing adoption across residential, commercial, and utility sectors, positioning solar energy as a cornerstone of Australia's clean energy future.
Grab a sample PDF…
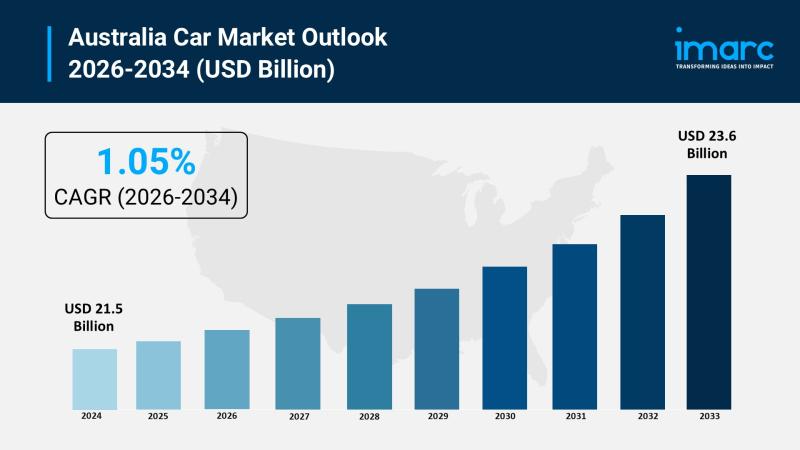
Australia Car Market 2026 | Surge to Grow to USD 23.6 Billion by 2034
Market Overview
The Australia car market reached a size of USD 21.5 Billion in 2025 and is forecasted to grow to USD 23.6 Billion by 2034. The market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 1.05% throughout the forecast period from 2026 to 2034. Growth is driven primarily by increasing demand for electric vehicles, SUVs, and connected car technologies, spurred by environmental awareness, lifestyle changes, and technological innovation toward sustainable…
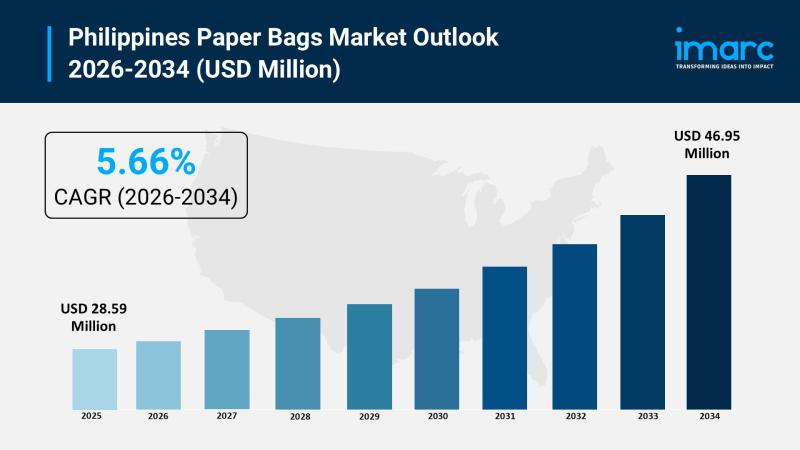
Philippines Paper Bags Market 2026 | Expected to Reach USD 46.95 Million by 2034
Market Overview
The Philippines paper bags market size was valued at USD 28.59 Million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 46.95 Million by 2034, with a growth rate of 5.66% CAGR from 2026 to 2034. This growth is driven by increasing environmental concerns, government bans on single-use plastics, and rising adoption by retailers and foodservice providers. The expanding food and beverage sector, coupled with heightened awareness of plastic pollution,…
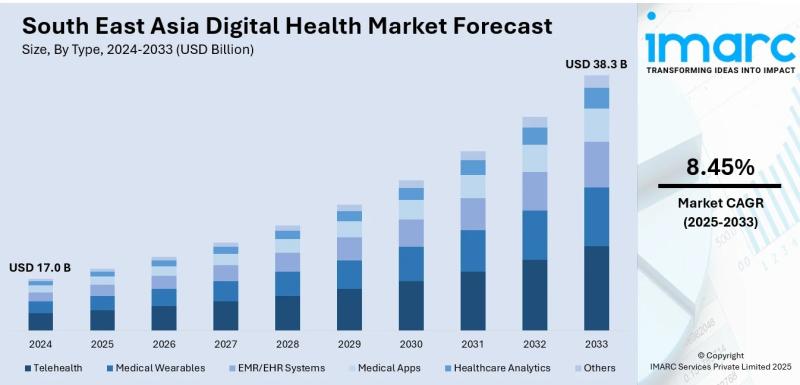
South East Asia Digital Health Market Size, Share, Trends, Growth & Insights 202 …
According to IMARC Group's report titled "South East Asia Digital Health Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Component, and Country, 2025-2033" the report offers a comprehensive analysis of the industry, including market share, growth, trends, and regional insights.
South East Asia Digital Health Market Analysis
The South East Asia digital health market size reached USD 17.0 Billion in 2024. The market is forecast to reach USD 38.3 Billion by 2033,…
More Releases for Production
Production Printers Market Report 2024 - Production Printers Market Demand And T …
"The Business Research Company recently released a comprehensive report on the Global Production Printers Market Size and Trends Analysis with Forecast 2024-2033. This latest market research report offers a wealth of valuable insights and data, including global market size, regional shares, and competitor market share. Additionally, it covers current trends, future opportunities, and essential data for success in the industry.
According to The Business Research Company's, The production printers market size…
Introducing Production Solved: Your Partner for Event Production and Corporate V …
New York, NY- Production Solved, a leading event production company, is thrilled to announce its comprehensive services for event production and corporate video production. With an unwavering commitment to excellence and a team of seasoned professionals, Production Solved aims to deliver exceptional experiences that captivate audiences and elevate brands.
As businesses navigate the dynamic landscape of events and corporate communications, the demand for top-notch production services has never been greater. Production…
Fertilizer Catalyst Market to Undertake Strapping Growth During 2018 to 2028(Seg …
Global Fertilizer Catalyst Market Introduction
Rising demand for catalysts is being witnessed from the fertilizer industry. Fertilizer catalysts are various kinds of metal oxides which are used for increasing the reaction rate in the fertilizer industry. Fertilizer catalysts are primarily used during ammonia production. Fertilizer catalysts find applications in processes including methanol production, ammonia production, formaldehyde production, syngas production and others. The activity of the fertilizer catalyst decides the yield and…
Fertilizer Catalyst Market to Showcase Vigorous Demand during the Period until 2 …
Global Fertilizer Catalyst Market Introduction
Rising demand for catalysts is being witnessed from the fertilizer industry. Fertilizer catalysts are various kinds of metal oxides which are used for increasing the reaction rate in the fertilizer industry. Fertilizer catalysts are primarily used during ammonia production. Fertilizer catalysts find applications in processes including methanol production, ammonia production, formaldehyde production, syngas production and others. The activity of the fertilizer catalyst decides the yield and…
Semiconductor Production Equipment Market - Increasing Electronics Production Wo …
Global Semiconductor Production Equipment Market: Snapshot
Global market for semiconductor production equipment has been covered under the scope of this report. Semiconductor production equipment (SPE) is used in possibly the most advanced and complex manufacturing process in the world, which is, the production of semiconductor devices. Semiconductor products, such as memory devices and microprocessors are used in a wide range of devices such as personal computers, consumer electronics and telecommunications equipment.…
Vacuum Pumps Market Forecast by Production Value, Capacity and Production
Big Market Research Add New “Vacuum Pumps Market” Research Report to It’s a Database.
Request sample report @ https://goo.gl/cajJ1x
The report provides a basic overview of the Vacuum Pumps industry including definitions, classifications, applications and industry chain structure. And development policies and plans are discussed as well as manufacturing processes and cost structures.
This report studies Vacuum Pumps focuses on top manufacturers in global market, with capacity, production, price,…
