Press release
How to Solve Pigment Agglomeration and Improve Dispersion in Plastic Color Masterbatches
In the plastics industry, color masterbatch is the most common and efficient method for coloring polymers. However, achieving uniform color distribution remains a persistent challenge. Uneven dispersion not only affects product appearance but also reduces mechanical strength and production efficiency - issues that cost manufacturers time, material, and customer trust.This article explores the role of additives in color masterbatches, the root causes of pigment agglomeration, and introduces an effective solution - SILIKE Silicone Hyperdispersant SILIMER 6200 [https://www.siliketech.com/silicone-hyperdispersants-silimer-6200-for-hffr-cables-compounds-tpe-the-preparation-of-color-concentrates-and-technical-compounds-product/], designed to elevate color uniformity and processing performance.
What Are Additives in Color Masterbatches and Why They Matter
A color masterbatch typically contains three core components - pigments, carrier resins, and functional additives. While pigments provide color, additives determine how that color behaves during processing.
Additives in masterbatches can be grouped into three main categories:
1. Processing Aids: Enhance melt flow, reduce die build-up, and improve dispersion uniformity. Common examples include polyolefin waxes (PE/PP wax) and silicone-based additives.
2. Performance Enhancers: Protect pigments and resins from oxidation and aging while improving transparency, toughness, and gloss.
3. Functional Additives: Deliver special properties such as anti-static behavior, matte surface, flame retardancy, or biodegradability.
Selecting the right additive ensures not only vivid and stable color but also smoother production and reduced waste.
The Hidden Challenge: Pigment Agglomeration and Its Root Causes
Pigment agglomeration occurs when pigment particles, due to high surface energy and van der Waals forces, clump together into larger secondary particles. These aggregates are difficult to break apart, leading to visible color streaks, specks, or uneven shading in molded or extruded products.
Common causes include:
- Incomplete wetting of pigment particles by the carrier resin
- Electrostatic attraction and density mismatch between components
- Inadequate shear force during mixing
- Poor dispersion system design or insufficient processing temperature
- Lack of effective dispersant or incompatibility with the resin matrix
The result: color inconsistency, reduced tinting strength, and poor mechanical integrity.
Proven Methods to Achieve Uniform Color Distribution
Achieving excellent dispersion requires both scientific understanding and precise processing control. The process involves three key stages - wetting, de-agglomeration, and stabilization.
1. Wetting: The dispersant must fully wet the pigment surface, replacing air and moisture with compatible resin.
2. De-agglomeration: High shear and impact forces break down agglomerates into fine primary particles.
3. Stabilization: A protective molecular layer around each pigment particle prevents re-agglomeration, ensuring long-term dispersion stability.
Practical approaches:
- Use optimized twin-screw extrusion and mixing parameters
- Pre-disperse pigments before masterbatch compounding
- Introduce high-efficiency dispersants such as silicone-modified materials to improve pigment wetting and flowability
Effective Solution: Additives and Pigment Dispersion Technology in Plastic Masterbatches SILIKE Hyperdispersant Silimer 6200
To overcome the limitations of conventional wax-based dispersants, SILIKE developed the SILIMER 6200 Silicone Hyperdispersant - a novel silicone-based lubricant engineered for high-performance color masterbatches and compounds.
Image: https://www.siliketech.com/uploads/Additives-and-Pigment-Dispersion-Technology-in-Plastic-Masterbatches-SILIKE-Hyperdispersant-Silimer-6200.png
SILIMER 6200 is a modified silicone wax [https://www.siliketech.com/silicone-hyperdispersants-silimer-6200-for-hffr-cables-compounds-tpe-the-preparation-of-color-concentrates-and-technical-compounds-product/]that serves as an effective hyperdispersant-an efficient solution to uneven pigment dispersion in color masterbatches.
This masterbatch is specially developed for HFFR cable compounds, TPE, the preparation of color concentrates, and technical compounds. It provides excellent thermal and color stability, and exerts a positive influence on masterbatch rheology. By improving filler wetting and infiltration, SILIMER 6200 enhances pigment dispersion, increases productivity, and reduces coloration costs.
It is suitable for use in polyolefin-based masterbatches (especially PP), engineering compounds, plastic masterbatches, filled modified plastics, and filled compounds.
Masterbatch processing aid SILIMER 6200 combines the molecular characteristics of silicone and organic segments, enabling it to migrate to pigment interfaces where it significantly reduces interfacial tension and enhances pigment-resin compatibility.
Key Benefits of Hyperdispersant SILIMER 6200 [https://www.siliketech.com/silicone-hyperdispersants-silimer-6200-for-hffr-cables-compounds-tpe-the-preparation-of-color-concentrates-and-technical-compounds-product/] for color masterbatch solutions:
Enhanced pigment dispersion: Breaks down pigment clusters and stabilizes fine distribution
Improved coloring strength: Achieves brighter, more consistent shades with less pigment loading
Prevention of filler and pigment reunion: Maintains stable color uniformity during processing
Better rheological properties: Increases melt flow and processability for easier extrusion or molding
Higher production efficiency: Reduces screw torque and cycle time, lowering overall costs
Broad Compatibility:
SILIKE dispersant SILIMER 6200 works effectively with a wide range of polymers including PP, PE, PS, ABS, PC, PET, and PBT, making it a versatile solution for multiple masterbatch and compounding applications.
Final Thoughts: Masterbatch Quality Starts from the Right Additive
In color masterbatch production, dispersion quality defines product value. Understanding pigment behavior, optimizing processing parameters, and selecting high performance silicone and siloxane additives like functional additive SILIMER 6200 are crucial steps toward achieving consistent, high-performance coloration.
Whether you are developing single-pigment concentrates or customized color compounds, SILIKE's silicone-based hyperdispersant technology offers a proven way to eliminate color streaks, enhance color strength, stability, and production efficiency - helping you deliver superior products with confidence.
Discover more about silicone hyperdispersant solutions for masterbatches: Visit www.siliketech.com [https://www.siliketech.com/contact-us/] or contact amy.wang@silike.cn for detailed technical guidance and formulation support.
Media Contact
Company Name: Chengdu Silike Technology Co., Ltd.
Email:Send Email [https://www.abnewswire.com/email_contact_us.php?pr=how-to-solve-pigment-agglomeration-and-improve-dispersion-in-plastic-color-masterbatches]
Country: China
Website: https://www.siliketech.com/
Legal Disclaimer: Information contained on this page is provided by an independent third-party content provider. ABNewswire makes no warranties or responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you are affiliated with this article or have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article and would like it to be removed, please contact retract@swscontact.com
This release was published on openPR.
Permanent link to this press release:
Copy
Please set a link in the press area of your homepage to this press release on openPR. openPR disclaims liability for any content contained in this release.
You can edit or delete your press release How to Solve Pigment Agglomeration and Improve Dispersion in Plastic Color Masterbatches here
News-ID: 4269646 • Views: …
More Releases from ABNewswire
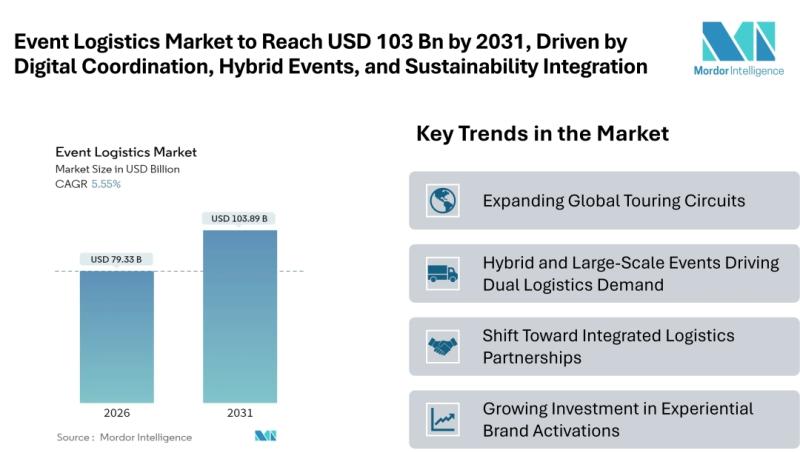
Event Logistics Market to Reach USD 103.89 Billion by 2031, Driven by Digital Co …
Mordor Intelligence has published a new report on the Event Logistics Market, offering a comprehensive analysis of trends, growth drivers, and future projections.
Event Logistics Market Overview
According to Mordor Intelligence, the event logistics market size [https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/global-event-logistics-market?utm_source=abnewswire] stood at USD 75.16 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 79.33 billion in 2026 to USD 103.89 billion by 2031, registering a CAGR of 5.55% during 2026-2031. Expansion is being driven…
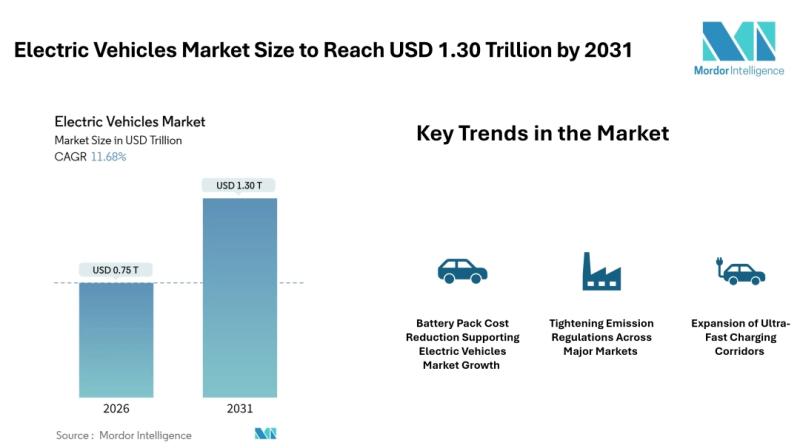
Electric Vehicles Market Size to Reach USD 1.30 Trillion by 2031, Driven by Batt …
Mordor Intelligence has published a new report on the electric vehicles market, offering a comprehensive analysis of trends, growth drivers, and future projections.
Electric Vehicles Market Overview
According to Mordor Intelligence, the electric vehicles market size [https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/electric-vehicle-market?utm_source=abnewswire] reached USD 0.75 trillion in 2026 and is projected to grow to USD 1.30 trillion by 2031, registering a CAGR of 11.68% during the forecast period. The electric vehicles market growth is supported by falling…
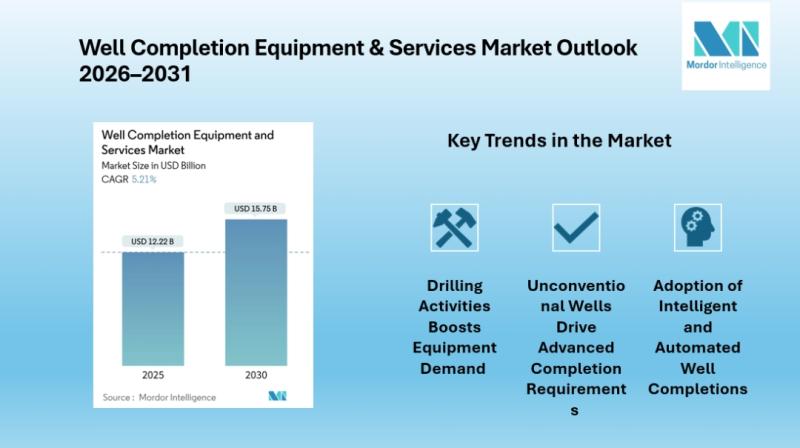
Global Well Completion Equipment and Services Market Set to Expand to USD 15.75 …
Mordor Intelligence has published a new report on the Well Completion Equipment and Services Market, offering a comprehensive analysis of trends, growth drivers, and future projections
The global well completion equipment and services market [https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/well-completion-equipment-and-services-market?utm_source=abnewswire] is projected to grow steadily over the coming years, reaching an estimated USD 15.75 billion by 2030, up from USD 12.22 billion in 2025. This growth, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of approximately 5.21%, is…

Why Is the Low Earth Orbit Satellite Market Gaining Strategic Importance?
The low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite market was valued at $11,221,800 thousand in 2024 and is projected to reach $254,000 thousand by 2035.
The global Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellite Market is reshaping modern space communications and digital infrastructure, supported by advances in satellite technology, reduced launch costs, and growing adoption across commercial and government sectors. Rising demand for low-latency broadband, Earth observation, and IoT connectivity is accelerating market momentum. As…
More Releases for SILIMER
Facing Die Build-Up, Rough Surfaces, and Low Output? Here's the PFAS-Free Way to …
HDPE and MDPE pipes form the backbone of modern water infrastructure - delivering safe, durable, and high-pressure performance.
Yet during extrusion, manufacturers often face recurring issues: die build-up, melt fracture, unstable back pressure, and inconsistent surface finish. These problems not only affect pipe appearance but also reduce line speed, increase maintenance downtime, and raise energy costs.
For decades, fluoropolymer-based processing aids such as 3M Trademark Dynamar Trademark PPA have been used to…
India Considers Banning PFAS in Food Packaging: What Manufacturers Should Know
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has proposed major amendments to the Food Safety and Standards (Packaging) Regulations, 2018. This draft, released on 6 October 2025, signals a potential ban on PFAS ("forever chemicals") and BPA in food-contact materials - including burger wrappers, beverage bottles, and other single-use packaging.
The FSSAI has invited public and stakeholder comments over a 60-day period before finalizing the amendment.
This move aligns India…
How to Improve Mold Release and Lubrication in Clear PC Compounds?
Transparent polycarbonate (PC) is widely used in high-end applications such as optical lenses, light covers, medical devices, and consumer electronics due to its excellent transparency, toughness, and heat resistance. However, processing transparent PC poses significant challenges, particularly in achieving smooth mold release and consistent internal lubrication.
What Makes Transparent PC So Popular-And So Challenging to Process?
Transparent PC offers exceptional optical clarity and impact strength, making it ideal for parts requiring aesthetics…
Enhance EVA Film Production with SILIKE SILIMER 2514E
EVA film, short for Ethylene Vinyl Acetate film, is a versatile material made from a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. It's widely used across various industries due to its unique properties, such as flexibility, transparency, durability, and strong adhesion. The vinyl acetate content in EVA can be adjusted during production, allowing manufacturers to tailor its characteristics, like softness, toughness, or clarity, to suit specific applications. Common uses include solar…
The Application of Silicone Release Agents in Engineering Plastics
In the field of modern engineering plastics processing, silicone release agents have emerged as a crucial component, playing a significant role in enhancing production efficiency and product quality.
Silicone release agents [https://www.siliketech.com/silimer-series-silicone-wax/] are known for their excellent release properties. When applied to the surface of engineering plastics molds, they form a thin, uniform film. This film effectively reduces the adhesion between the plastic part and the mold surface during the molding…
Silicone additives specially developed for inks and coatings enhance scratch res …
Inks and coatings are two common chemical products that have a wide range of applications in several fields.
Ink is a homogeneous mixture of pigments and linkers used for printing, which can be transferred to different substrates (e.g., paper, plastic, metal, etc.) through a printing press to form images or text. There are many types of inks, which can be categorised according to their use, composition and drying method. They are…
