Press release
New Technology of PROTACs
Most of the drugs currently in clinical use are based on small molecules and use the "occupancy-driven" mode of action to inhibit the function of proteins and play a role in the treatment of diseases. Different from traditional small molecule inhibitors and antagonists, protein degradation technology has developed rapidly in recent years because of its ability to induce the degradation of therapeutic target proteins, providing a new idea for the development of new drugs.PROTACs (Proteolysis-targeting Chimeras), which was first proposed by Crews et al in 2001, can reduce protein levels rather than inhibit protein functions by taking advantage of the natural protein cleaning system in the body. PROTAC is a heterobifunctional molecule with one end connected to a ligand that binds the target protein, one end to an E3 ubiquitin ligase, and a suitable Linker in the middle. PROTAC degradation of target proteins is achieved through the ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS).
Since PROTACs were developed on the basis of POI inhibitors, they still have a certain degree of off-target effects. Second, due to the large molecular weight of PROTAC, its poor cell membrane permeability and poor pharmacokinetic (PK) properties greatly reduce its biological and therapeutic effects. In addition, although some PROTACs can effectively induce the degradation of target proteins, their biological effects are weak and have no effective effect on disease. Finally, most proteins do not have corresponding small molecule conjugates to design PROTACs, such as transcription factors that play an important role in disease development. Since there are few inhibitors of transcription factors, there is no binder available when designing PROTACs targeting transcription factors. This greatly limits the application of PROTAC technology. In order to solve the above problems, different types of PROTAC technologies have emerged in recent years, such as Antibody-PROTAC, Aptamer-PROTAC conjugates, Dual-target PROTACs, Folate-caged PROTACs and TF-PROTACs.
Antibody-PROTAC
Antibody-PROTAC is a new strategy to explore the assembly of new antibody-PROTAC conjugates in combination with antibodies. This technology enables specific degradation of proteins in different cells and tissues, thereby optimizing and maximizing the therapeutic window, reducing the side effects of broad-spectrum PROTACs, and increasing their potential as drugs or chemical tools.
Aptamer-PROTAC conjugates
Aptamers are single-stranded nucleic acids with complex three-dimensional structures, mainly including stems, loops, hairpins and G4 polymers. They bind to target proteins through special effects such as hydrogen bonds, base stacking forces, electrostatic effects, etc., with high specificity and affinity, and can improve the water solubility, membrane permeability, and tumor targeting of traditional PROTACs.
Dual-target PROTACS
In the occurrence and development of cancer, there are usually multiple factors that work together, including different kinds of kinases and growth factors, which can act independently or interfere with each other through signaling networks. This method is mainly to design a single molecule that binds two or more pharmacophore, and simultaneously targets two or more anti-tumor targets.
Folate-caged PROTACs
Folate receptor alpha (FOLR1) is low in normal tissues but highly expressed in many human cancers. Folic acid caged PROTACs is another technology to improve the targeting specificity of PROTACs. The basic principle is to introduce folic acid groups into PROTAC molecules to achieve release in target cells and tissues. In this technique, folic acid releases active PROTAC through the action of endogenous hydrolase in the cell, and then the degradant induces the degradation of the target protein.
TF-PROTACs
Transcription factors (TFs) are a class of proteins involved in gene expression and regulation, and are also potential targets for tumor therapy. Transcription factors, unlike traditional kinases, do not have activity pockets or allosteric regulatory sites commonly found in kinases or other enzymes, making them difficult to target by small molecule inhibitors. Since TFs can bind to specific DNA sequences and regulate the transcription process, it is theoretically possible to target TFs with different DNA sequences instead of small molecule inhibitors. Therefore, TF-PROTAC replaces the small molecule ligand of the targeting protein with the corresponding DNA sequence to form TF-PROTAC, which targets specific TF and induces its degradation, thereby regulating the level and biological function of specific TF.
As a professional PEG derivatives supplier, Biopharma PEG is dedicated to the R&D of PROTAC Linker, providing high purity PEG linkers with various reactive groups to continuously assist your project development.
Biopharma PEG Scientific Inc.
Address: 108 Water Street, Room 4D, Watertown, MA 02472, USA
TEL: 1-857-366-6766
Fax: 617-206-9595
Email: sales@biochempeg.com
Website: https://www.biochempeg.com/
Biopharma PEG Scientific Inc. is a biotechnology-oriented company in Watertown, Massachusetts. We are dedicated to manufacturing and supplying high purity monodispersed and polydispersed polyethylene glycol (PEG) derivatives and PEG raw material, PEGylation services, and custom PEG derivative synthesis to clients worldwide. We continuously expand the capability to provide large-scale manufacture of high purity PEG derivatives with an extensive variety of functional groups, in both non-GMP and GMP grade. These PEG linkers have been widely used in bioconjugation, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) therapeutic, click chemistry, 3d bioprinting, drug delivery and diagnostics field, etc.
This release was published on openPR.
Permanent link to this press release:
Copy
Please set a link in the press area of your homepage to this press release on openPR. openPR disclaims liability for any content contained in this release.
You can edit or delete your press release New Technology of PROTACs here
News-ID: 2688813 • Views: …
More Releases from Biopharma PEG Scientific Inc.

Biopharma PEG Supplies Cholesterol (Plant-Derived) Used As Excipients for Lipid …
Cholesterol, a derivative of cyclopentane polyhydrophenanthrene, is the main steroid compound in mammals. Most of the traditional cholesterol comes from animal brainstem and lanolin, which is of animal origin and has the risk of carrying animal viruses. Biopharma PEG innovatively uses plant sterols as starting materials to prepare plant-derived cholesterol (CAS NO.: 57-88-5) through biological fermentation and green synthesis, eliminating the generation and carrying of viruses from the source.
Cholesterol has…
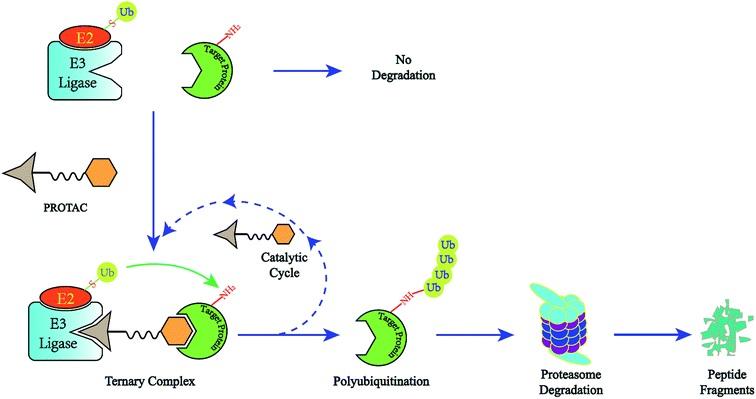
Development Trends And Potential Challenges of PROTACs
PROTAC technology has been in development for more than 20 years. PROTAC proof-of-concept studies date back to 2001, when Crews' team tested the possibility of artificially induced intracellular protein degradation with a peptide that was too large in molecular weight and required cells to penetrate the peptide to improve cell permeability. The discovery of the first small molecule PROTAC and the subsequent small molecule E3 ligand, reported in 2008, greatly…
ADC Drugs For Breast Cancer Treatment
Breast cancer is the malignant tumor with the highest morbidity and mortality among women worldwide. At present, the main therapeutic methods include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, endocrine therapy and targeted therapy, etc. The development and marketing of new drugs have far-reaching significance in improving the survival of breast cancer patients and changing the pattern of breast cancer treatment.
On February 24, 2023, The NMPA approved Enhertu, an injectable drug developed jointly by…
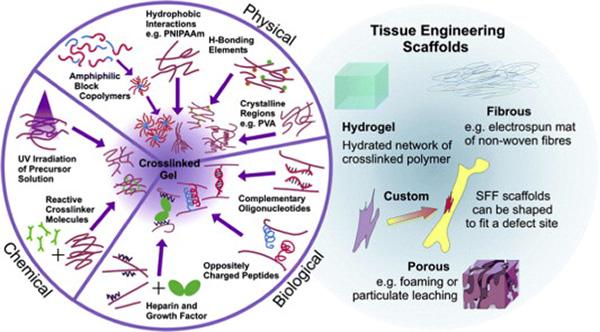
History Development of Hydrogels
Hydrogels are composed of hydrophilic polymers, whose three-dimensional network structure can not only absorb a large amount of water, but also be used to carry drugs. Hydrogels prepared with suitable materials have the characteristics of high biocompatibility, mechanical and viscoelastic control. Since the term was coined in the late 19th century, hydrogels have been widely used in drug delivery, wound dressing, tissue engineering, and hygiene products. This article mainly introduces…
More Releases for PROTAC
Proteolysis Targeting Chimera Protac Market Gains Traction Amid Technological Ad …
New Jersey, US State: "The global Proteolysis Targeting Chimera Protac market in the Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals category is projected to reach USD 5.3 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 23.5% from 2025 to 2031. With rising industrial adoption and continuous innovation in Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals applications, the market is estimated to hit USD 1.2 billion in 2024, highlighting strong growth potential throughout the forecast period."
Proteolysis Targeting Chimera (PROTAC)…
PROTAC Market to See Booming Growth 2025-2032 | Arvinas, Celgene, Nurix Therapeu …
The Global PROTAC Market is estimated to be valued at USD 0.50 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 2.42 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25.3% from 2025 to 2032.
According to the latest research from CoherentMI, the PROTAC Market is projected to experience significant growth between 2025 and 2032. This market intelligence report offers in-depth analysis based on thorough research,…
The PROTAC market is anticipated to experience robust expansion over the forecas …
(Albany, USA) DelveInsight's PROTAC Market Insights report offers an in-depth analysis of existing treatment approaches, upcoming PROTAC therapies, the market share of each therapy, and projected as well as current market size for PROTACs from 2020 to 2034. The data is segmented across the 7 major markets (7MM), including the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The PROTAC market is anticipated to expand considerably…
PROTAC Market Set Transforming Therapeutics for Explosive Growth in Targeted Dru …
A new report published by CoherentMI, titled "PROTAC Market: Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2024-2031," offers a comprehensive analysis of the industry, which comprises insights on the PROTAC market analysis. The report also includes competitor and regional analysis, and contemporary advancements in the market.
The Global PROTAC Market is estimated to be valued at USD 0.40 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.59 billion by…
PROTAC Market Industry Trends, Growth Projections, and Market Share Report 2024 …
A new Report by CoherentMI Market Reports, titled "PROTAC Market: Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2024-2031," offers a comprehensive analysis of the industry, which comprises insights on the PROTAC market analysis. The report also includes competitor and regional analysis, and contemporary advancements in the market.
The Global PROTAC Market is estimated to be valued at USD 0.40 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 2.59 billion…
PROTAC Cancer Therapy PROTAC Drugs Clinical Trials Insight
Global Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras PROTAC Therapy Clinical Trials Insight & Market Opportunity Report Highlights:
• First PROTAC Drug Approval Expected By 2027
• Insight On More Than 50 PROTAC Drugs In Clinical Trials
• Global PROTAC Drugs Clinical Trials Insight By Company, Country, Indication & Phase
• Orphan & Fast Track Designation Insight
• PROTAC Drugs Clinical Application & Development Outlook By Indication
• Current & Future Market Overview
• Global PROTAC Drug Market Dynamics
Download Report: https://www.kuickresearch.com/ccformF.php?t=1728551968
PROTACs, or proteolysis-targeting chimeras, have emerged as a…
