Press release
Battery Charger Manufacturing Plant Cost 2026: Comprehensive Project Report, Feasibility Study and Industry Outlook
The global battery charger manufacturing industry represents a critical enabler of the electrification revolution, positioned at the convergence of consumer electronics proliferation, electric vehicle adoption acceleration, and renewable energy storage expansion. As rechargeable batteries become increasingly ubiquitous across personal devices, transportation systems, industrial equipment, and energy infrastructure, battery chargers have emerged as indispensable components ensuring reliable power replenishment and optimal battery performance. This comprehensive guide provides an authoritative exploration of the technical, financial, and strategic dimensions of establishing a battery charger manufacturing plant, leveraging current market intelligence and industry insights to support informed investment decision-making in this rapidly evolving and commercially vital electronics manufacturing sector.Market Overview and Growth Potential
The battery charger manufacturing sector is experiencing robust and accelerating growth driven by powerful, interconnected market forces that reflect fundamental transformations in energy consumption, mobility, and technology utilization patterns. The industry's expansion is propelled by several critical factors:
• Rising use of consumer electronics requiring frequent charging
• Electric vehicle adoption creating massive charging infrastructure demand
• Renewable energy storage systems requiring battery management solutions
• Power tools and cordless equipment proliferation in industrial and consumer markets
• UPS systems and backup power solutions for critical applications
• Favorable government incentives for EV adoption
• Growing awareness of energy-efficient charging solutions
The global battery charger market was valued at USD 28.04 Billion in 2025, establishing a substantial foundation for sector growth. According to comprehensive market analysis, the industry is projected to reach USD 40.71 Billion by 2034, exhibiting a solid CAGR of 4.2% from 2026 to 2034. This consistent growth trajectory reflects the essential nature of charging infrastructure supporting the broader electrification megatrend transforming transportation, energy, and consumer technology.
The market expansion is fundamentally driven by the electric vehicle revolution reshaping global transportation. According to authoritative industry data, over 20% of new cars sold worldwide in 2024 were electric, with global sales exceeding 17 million units, representing a 25% increase from 2023. This dramatic EV adoption acceleration creates unprecedented demand for charging solutions spanning residential, commercial, and public charging infrastructure, as well as sophisticated on-board chargers integrated within vehicles.
Consumer electronics proliferation continues driving sustained charger demand as smartphones, laptops, tablets, wearables, and wireless devices become increasingly integral to personal and professional life. The shift toward cordless power tools, vacuum cleaners, and garden equipment in both consumer and professional markets further expands the addressable market for specialized battery charging solutions.
IMARC Group's report, "Battery Charger Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2026: Industry Trends, Plant Setup, Machinery, Raw Materials, Investment Opportunities, Cost and Revenue," offers a comprehensive guide for establishing a plant. The battery charger manufacturing plant cost report offers insights into the process, financials, capital investment, expenses, ROI, and more for informed business decisions.
Plant Capacity and Production Scale
The proposed battery charger manufacturing facility is designed with substantial production capacity and technological sophistication as core operational principles. The annual production capacity ranges between 5 to 10 million units, enabling significant economies of scale through high-volume production while maintaining the manufacturing flexibility necessary to serve diverse customer requirements across multiple charger types, voltage specifications, and application categories.
This capacity range positions the plant to serve multiple market segments effectively:
• Consumer Electronics: Chargers for smartphones, laptops, tablets, wearables, and personal devices
• Electric Vehicles: Charging units for EV batteries, on-board chargers, and auxiliary systems
• Renewable Energy Systems: Battery charging solutions for solar and wind storage applications
• Industrial Equipment: Chargers for power tools, forklifts, material handling equipment, and machinery
• Backup Power Systems: UPS battery chargers and inverter charging solutions for critical infrastructure
The production facility can manufacture diverse charger types addressing varied functional requirements:
• Basic linear chargers: Simple, cost-effective designs for basic applications
• Smart chargers with microcontrollers: Sophisticated charging management with overcharge protection, temperature monitoring, and adaptive charging protocols
• Fast-charging units: High-power chargers enabling rapid battery replenishment
• Multi-chemistry chargers: Versatile designs compatible with different battery types (lithium-ion, lead-acid, NiMH, NiCd)
• Wireless charging solutions: Inductive charging systems for consumer electronics
• Industrial charging systems: Heavy-duty chargers for commercial and industrial battery applications
Request for a Sample Report: https://www.imarcgroup.com/battery-charger-manufacturing-plant-project-report/requestsample
Financial Viability and Profitability Analysis
The battery charger manufacturing business demonstrates exceptionally compelling financial fundamentals supported by rapidly growing end-market demand, technological advancement opportunities, and favorable profit margin characteristics compared to many electronics manufacturing segments. The project offers robust profitability potential with gross profit margins typically ranging between 30-40%, driven by efficient production processes leveraging automation, economies of scale through high-volume manufacturing, and premium pricing opportunities for advanced smart charging and fast-charging technologies.
Net profit margins are projected at 12-18%, reflecting operational efficiency achievable through optimized manufacturing processes, strategic component procurement, surface-mount technology (SMT) automation reducing labor intensity, and effective capacity utilization management. These margin profiles significantly exceed many commodity electronics categories and demonstrate the value-added nature of sophisticated charging technology incorporating intelligent power management, safety features, and user-friendly interfaces.
The financial projections developed for this project incorporate comprehensive analysis across all investment and operational dimensions. Capital investment modeling addresses land acquisition and facility development, specialized manufacturing facility construction with ESD-safe production environments, significant machinery procurement including SMT lines, wave soldering equipment, reflow ovens, automated optical inspection (AOI) systems, testing and programming stations, and packaging automation, utilities infrastructure supporting electronics manufacturing operations, and working capital for component inventory and operational expenses.
Operating cost analysis encompasses raw material expenses dominated by PCBs, integrated circuits, transformers, capacitors, resistors, and other electronic components, plastic or metal enclosure materials, cables and connectors, utility consumption for electronics manufacturing operations, labor costs for production operators, quality control technicians, and firmware programming specialists, equipment maintenance, component testing and validation, and distribution expenses for finished products.
These detailed financial models provide stakeholders with transparent visibility into project economics, including comprehensive capital expenditure (CapEx) breakdowns by equipment category, operating expenditure (OpEx) structures with component price sensitivity analysis given electronics industry pricing dynamics, income projections across charger types and market segments, expected return on investment (ROI) under various capacity utilization and product mix scenarios, net present value (NPV) calculations, payback period analysis, and long-term profitability trajectories supporting strategic planning and investment decision-making.
Operating Cost Structure
Understanding the operating cost structure is fundamental to effective business planning and margin management in battery charger manufacturing. The cost architecture reflects component intensity, electronics manufacturing process requirements, and the technology-embedded nature of modern charging solutions.
In battery charger manufacturing operations, raw materials account for approximately 70-80% of total operating expenses (OpEx), with printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electronic components representing the predominant cost elements.
Key Raw Materials Include:
• Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): Core platform for component mounting and electrical interconnection
• Transformers: Power conversion components stepping down or isolating input voltage
• Capacitors: Energy storage and filtering components ensuring stable operation
• Integrated circuits (ICs): Microcontrollers, power management ICs, and control chips enabling smart charging features
• Resistors, diodes, MOSFETs: Discrete components for voltage regulation and circuit protection
• Casings: Plastic or metal enclosures providing physical protection and user interface
• Cables and connectors: Output cables, power plugs, and battery connectors
Utilities represent 5-10% of OpEx, covering electricity for manufacturing equipment operation, climate control maintaining appropriate temperature and humidity for electronics assembly, and compressed air for pneumatic pick-and-place systems. The relatively modest utility allocation reflects the less energy-intensive nature of electronics assembly compared to heavy manufacturing.
Additional operating costs encompass:
• Transportation for component delivery from electronics suppliers and finished product distribution to retailers, OEMs, and distributors
• Packaging materials for retail packaging, protective foam, and carton boxing
• Salaries and wages for SMT machine operators, quality control inspectors, firmware programmers, and test technicians
• Depreciation on substantial capital investments in SMT lines and testing equipment
• Component testing and validation costs ensuring reliability
• Firmware development and programming costs for smart chargers
• Regulatory compliance including safety certifications (UL, CE, FCC) and energy efficiency standards
Component procurement strategies represent critical success factors given electronics industry pricing volatility and supply chain complexity. Strategic considerations include establishing relationships with authorized component distributors and original component manufacturers, negotiating volume-based pricing for high-consumption components, maintaining optimal component inventory balancing carrying costs against supply availability, implementing vendor-managed inventory (VMI) for critical components, and potentially exploring direct relationships with integrated circuit manufacturers for proprietary charging ICs.
Capital Investment Requirements
Establishing a battery charger manufacturing plant requires substantial capital investment reflecting the electronics manufacturing sophistication, precision assembly requirements, and comprehensive testing infrastructure essential for producing reliable, safety-certified charging products.
Capital Expenditure Components:
• Land and Site Development Costs: Industrial land acquisition, site preparation for electronics manufacturing
• Civil Works Costs: Manufacturing facility construction with ESD-safe flooring, climate control, clean assembly areas
• Machinery Costs: Largest portion of CapEx representing sophisticated electronics manufacturing equipment
• Other Capital Costs: Testing equipment, firmware development tools, initial component inventory, regulatory certifications
Site Selection Considerations:
Strategic location selection must evaluate several critical factors:
• Easy access to key raw materials including PCBs from board fabrication suppliers, electronic components from distributors or manufacturers, and enclosure materials from injection molding or metal fabrication suppliers
• Proximity to target markets particularly consumer electronics distribution centers, automotive supply chains, and industrial equipment manufacturers minimizing distribution costs and supporting just-in-time delivery
• Robust infrastructure including reliable electricity supply essential for electronics manufacturing, adequate climate control capabilities, transportation networks, and telecommunications infrastructure supporting automated production monitoring
• Access to skilled labor with electronics assembly experience, SMT operation expertise, and quality control capabilities
• Compliance with local zoning laws and environmental regulations governing electronics manufacturing and waste disposal
• Space for future expansion accommodating additional SMT lines and product diversification
Essential Machinery Requirements:
High-quality, sophisticated equipment represents the technical and operational foundation:
• SMT (Surface Mount Technology) lines: Automated pick-and-place machines mounting components onto PCBs with precision positioning, representing the core production technology
• Wave soldering machines: Through-hole component soldering equipment for components not suitable for SMT assembly
• Reflow ovens: Controlled heating systems melting solder paste and creating permanent electrical connections
• Testing benches: Automated test equipment verifying electrical performance, safety compliance, and charging functionality
• Programming stations: Equipment for firmware uploading into microcontroller-based smart chargers
• Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems: Vision systems detecting assembly defects and component placement errors
• Automated packaging systems: Equipment for carton forming, product insertion, and sealing
Supporting infrastructure includes ESD (electrostatic discharge) protection systems preventing component damage, component storage with humidity control, quality control laboratories with oscilloscopes and power analyzers, and environmental test chambers for reliability validation.
Civil works costs encompass specialized facility construction with ESD-safe flooring preventing static discharge, climate-controlled production areas maintaining appropriate temperature and humidity, segregated areas for raw material storage and finished goods inventory, quality control and testing laboratories, and administrative offices. Other capital costs include comprehensive testing equipment for safety and performance validation, firmware development tools and licenses, initial inventory of electronic components representing substantial working capital, safety certifications and regulatory approvals (UL, CE, FCC, Energy Star), and contingency reserves.
Ask Analyst for Customization: https://www.imarcgroup.com/request?type=report&id=9176&flag=C
Manufacturing Process Overview
The battery charger manufacturing process involves sophisticated sequential operations designed to assemble electronic components into functional, safe, and reliable charging devices:
Unit Operations Involved:
• Circuit design: Engineering specification of electrical circuits, component selection, and PCB layout
• PCB fabrication: Either in-house or outsourced production of printed circuit boards with defined traces and pad layouts
• Component mounting (SMT/THT): Automated surface-mount technology placing components on PCB surfaces, followed by through-hole technology insertion for larger components
• Soldering: Reflow soldering for SMT components, wave soldering for through-hole components creating permanent electrical connections
• Firmware programming: Uploading control software into microcontrollers enabling smart charging features, temperature monitoring, and safety protocols
• Enclosure assembly: Installing populated PCBs into plastic or metal casings
• Wiring: Connecting output cables, power cords, and battery connectors
• Functional testing: Comprehensive testing verifying proper charging operation, voltage accuracy, current regulation, and safety feature activation
• Quality inspection: Visual inspection and automated optical inspection verifying assembly quality
• Labeling: Applying product labels, safety warnings, and regulatory compliance marks
• Packaging: Retail packaging or bulk packaging for OEM supply
Quality Assurance Criteria:
Comprehensive quality control systems must monitor component quality through incoming inspection, ensure assembly quality through AOI and manual inspection, verify electrical performance through functional testing at multiple stages, confirm safety compliance through protection feature validation (overcurrent, overvoltage, temperature cutoff), and maintain full traceability supporting warranty management and regulatory compliance.
Technical Tests:
Testing protocols include voltage output accuracy verification, current regulation testing across load conditions, efficiency measurement, thermal performance under continuous operation, electromagnetic interference (EMI) testing for regulatory compliance, safety feature validation (short circuit protection, overcharge protection, thermal cutoff), drop testing for mechanical durability, and accelerated life testing predicting field reliability.
Major Applications and Market Segments
Battery charger manufacturing serves multiple essential applications across diverse technology and industrial categories:
Primary Applications:
• Mobile phones, laptops, tablets: Consumer electronics charging supporting billions of devices globally
• Power tools: Cordless drill, saw, and equipment chargers for construction and DIY markets
• EV batteries: Electric vehicle charging systems including on-board chargers and external charging infrastructure
• UPS systems: Uninterruptible power supply battery charging for data centers, telecommunications, and critical infrastructure
• Solar energy storage: Battery charging systems for residential and commercial solar installations
• Medical equipment: Specialized chargers for portable medical devices and equipment
• Industrial batteries: Forklift chargers, material handling equipment, and industrial battery systems
End-Use Industries:
• Consumer electronics: Smartphones, computing, wearables, audio devices
• Electric vehicles: Automotive OEMs, charging infrastructure providers
• Renewable energy: Solar installation companies, energy storage system integrators
• Industrial equipment: Material handling, power tools, industrial automation
• Telecommunications: Cellular towers, data centers, network infrastructure
• Automotive: Traditional vehicle auxiliary battery chargers, battery management systems
• Power backup systems: UPS manufacturers, emergency power system providers
The diversity of applications and end-market segments creates natural demand stability and reduces dependence on any single industry vertical or customer category.
Why Invest in Battery Charger Manufacturing?
Multiple strategic factors converge to make battery charger manufacturing an exceptionally attractive investment proposition:
✓ Expanding Adoption Across Industries: Increasing implementation of rechargeable batteries in consumer, industrial, and commercial sectors enhances the need for diverse charging solutions across power levels and application types.
✓ Strong Growth in Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy Storage: The rise of EVs (over 20% of new car sales globally) and renewable energy systems significantly boosts demand for efficient, intelligent, and high-power battery charging solutions.
✓ Continuous Innovation in Fast and Smart Charging Technologies: Advances in fast-charging capabilities, intelligent charging algorithms, temperature monitoring, battery health optimization, and wireless charging technologies enhance performance, safety, and user convenience while supporting premium pricing.
✓ Scalable Manufacturing with Automation Potential: Battery charger production can be scaled efficiently through SMT automation, robotic assembly, and automated testing, improving output consistency, reducing labor costs, and maintaining quality standards.
✓ High Demand for Customized and Application-Specific Chargers: Industries increasingly require chargers tailored to specific battery chemistries (lithium-ion, lead-acid, NiMH), capacity ranges, voltage specifications, and operational needs, creating opportunities for specialized solutions commanding premium pricing.
✓ Government Policy Support: Favorable government incentives for EV adoption, renewable energy deployment, and energy efficiency standards indirectly boost demand for charging infrastructure and efficient charging solutions.
✓ Energy Efficiency Regulations: Growing regulatory focus on charger efficiency (Energy Star, EU regulations) drives replacement of older, less efficient chargers and creates market opportunities for compliant products.
✓ Wireless Charging Adoption: Emerging wireless charging technologies for consumer electronics create new product categories and market expansion opportunities.
Industry Leadership
The global battery charger manufacturing industry features several established leaders with extensive production capacities and comprehensive product portfolios:
Leading Battery Charger Manufacturers:
• Battery Tender
• Ctek
• Delta-Q Technologies Corp.
• Interstate Batteries
• IOTA Engineering
• Lester Electrical
• Minn Kota
• NOCO
• ProMariner
• Quick USA
These established manufacturers serve end-use sectors including consumer electronics, electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, industrial equipment, telecommunications, automotive aftermarket, and power backup systems across global markets. Their market presence demonstrates the scalability and profitability potential of professional battery charger manufacturing operations while highlighting opportunities for new entrants to serve regional markets, develop specialized charging technologies, or differentiate through superior performance and customer service.
Buy Now: https://www.imarcgroup.com/checkout?id=9176&method=2175
Latest Industry Developments
The battery charger sector continues to experience rapid innovation and technological advancement:
• October 2025: Bel Fuse launched the BCF19-700-8, a 19.2 kW liquid-cooled on-board battery charger for hybrid and electric vehicles. Offering 94% efficiency, 450-900 VDC output range, and comprehensive protections against over-temperature, voltage, and current conditions, the charger supports CAN bus communication, rapid charging capabilities, and compatibility with diverse high-voltage battery systems.
• March 2025: BYD launched its Super e-Platform featuring Megawatt Flash Charging batteries and advanced charging infrastructure. The flash charging battery technology provides 400 km range in just 5 minutes of charging, matching gasoline refueling speeds and representing a breakthrough in charging convenience addressing key EV adoption barriers.
These developments underscore ongoing technological innovation, the industry's focus on ultra-fast charging addressing consumer range anxiety, and opportunities for manufacturers developing next-generation charging solutions supporting the EV revolution.
Conclusion
The battery charger manufacturing sector presents an exceptionally compelling investment opportunity characterized by strong market fundamentals, accelerating growth driven by electrification megatrends, attractive profit margins, and strategic positioning at the enabling infrastructure layer supporting the transformation of transportation, energy, and consumer technology.
For entrepreneurs and businesses seeking to participate in the electrification infrastructure enabling the transition to sustainable transportation and renewable energy, battery charger manufacturing offers a proven pathway to creating substantial value while supporting critical technological transitions. The sector's robust growth trajectory, supported by multiple structural demand drivers, technological advancement opportunities requiring continuous innovation, and favorable regulatory environment promoting electrification and efficiency, ensures continued market relevance and attractive opportunities for well-planned and professionally executed manufacturing ventures delivering consistent quality, technological sophistication, and operational excellence across diverse application segments.
Browse Related Reports:
Copper Anodes Manufacturing Plant Cost: https://industrytoday.co.uk/chemicals/comprehensive-report-on-copper-anodes-manufacturing-plant-line-market-dynamics-setup-cost-and-roi-forecast-2025
Bamboo Charcoal Manufacturing Plant Cost: https://industrytoday.co.uk/agriculture/bamboo-charcoal-manufacturing-plant-2025-project-cost-raw-materials-requirement-and-profit-margin
Stainless Steel Faucet Manufacturing Plant Cost: https://industrytoday.co.uk/market-research-industry-today/stainless-steel-faucet-manufacturing-plant-report-2025-unit-setup-cost-and-requirements-project-economics
Hdpe Pipe Manufacturing Plant Cost: https://industrytoday.co.uk/chemicals/hdpe-pipe-manufacturing-plant-report-2025-project-cost-raw-materials-requirement-and-unit-setup
Cyanide Production Plant Cost: https://industrytoday.co.uk/chemicals/cyanide-production-plant-2025-detailed-project-report-raw-materials-cost-and-unit-setup
About Us:
IMARC Group is a global management consulting firm that helps the world's most ambitious changemakers to create a lasting impact. The company provide a comprehensive suite of market entry and expansion services. IMARC offerings include thorough market assessment, feasibility studies, company incorporation assistance, factory setup support, regulatory approvals and licensing navigation, branding, marketing and sales strategies, competitive landscape and benchmarking analyses, pricing and cost research, and procurement research.
Services:
• Plant Setup
• Factoring Auditing
• Regulatory Approvals, and Licensing
• Company Incorporation
• Incubation Services
• Recruitment Services
• Marketing and Sales
Contact Us:
IMARC Group
134 N 4th St. Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
Email: sales@imarcgroup.com
Tel No:(D) +91 120 433 0800
United States: +1-201971-6302
This release was published on openPR.
Permanent link to this press release:
Copy
Please set a link in the press area of your homepage to this press release on openPR. openPR disclaims liability for any content contained in this release.
You can edit or delete your press release Battery Charger Manufacturing Plant Cost 2026: Comprehensive Project Report, Feasibility Study and Industry Outlook here
News-ID: 4371103 • Views: …
More Releases from IMARC Group
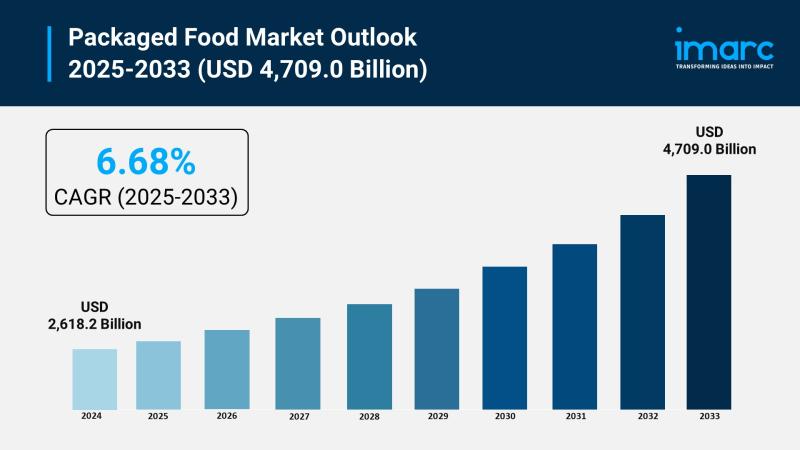
Packaged Food Market Size to Reach $4,709.0B by 2033: Insights & Trends
Market Overview:
The packaged food market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by surge in urbanization and hectic lifestyles, proliferation of e-commerce and digital retail, and government support and food security initiatives. According to IMARC Group's latest research publication, "Packaged Food Market: Global Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2025-2033", the global packaged food market size reached USD 2,618.2 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to…
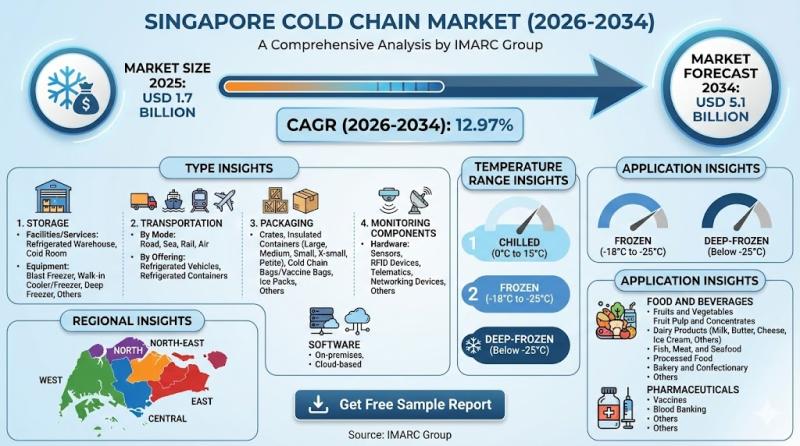
Singapore Cold Chain Market 2026-2034: $5.1B Industry Growth, Pharma Logistics & …
Source: IMARC Group | Category: Transportation and Logistics | Author Name: Tarang
Report Introduction
According to IMARC Group's latest report titled "Singapore Cold Chain Market Size, Share, Trends and Forecast by Type, Temperature Range, Application, and Region, 2026-2034", this study offers a granular analysis of the industry's shift towards temperature-controlled logistics for high-value perishable and pharmaceutical goods. The study offers a profound analysis of the industry, encompassing market share, size, Singapore cold…

Global Smart Electric Meter Market Size projected to Reach USD 48.6 Billion by 2 …
Market Overview
The global smart electric meter market was valued at USD 27.4 Billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 48.6 Billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.6% during the forecast period 2025-2033. The market's growth is driven by increasing investments in smart grid infrastructure, government initiatives for energy efficiency, urbanization, renewable energy integration, and advancements in IoT-enabled technologies for real-time energy management.
Study Assumption Years
• Base Year: 2024
• Historical…
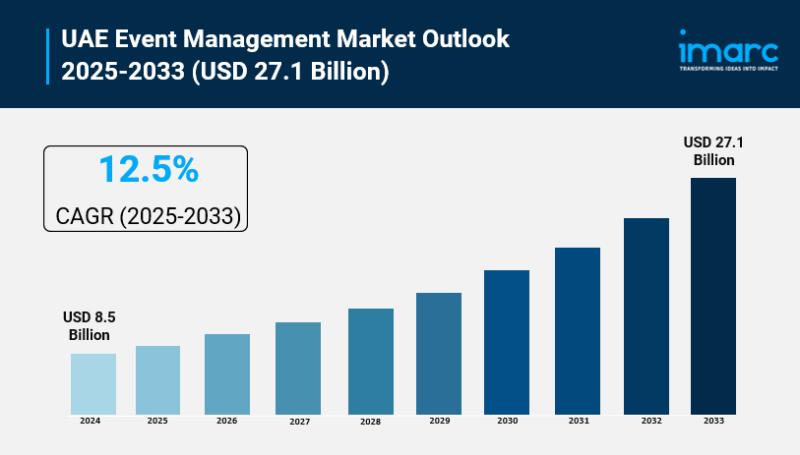
UAE Event Management Market Size To Exceed USD 27.1 Billion By 2033 | CAGR of 12 …
UAE Event Management Market Overview
Market Size in 2024: USD 8.5 Billion
Market Size in 2033: USD 27.1 Billion
Market Growth Rate 2025-2033: 12.5%
According to IMARC Group's latest research publication, "UAE Event Management Market: Industry Trends, Share, Size, Growth, Opportunity and Forecast 2025-2033", The UAE event management market size reached USD 8.5 Billion in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach USD 27.1 Billion by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate…
More Releases for Cost
Steel Production Cost - Process Economics, Raw Materials, and Cost Drivers
Steel is the backbone of modern industry, and its production cost is one of the most closely tracked indicators across construction, infrastructure, automotive, and manufacturing sectors. Unlike niche chemicals or APIs, steel economics are driven by scale, energy intensity, and raw material volatility.
Here's the thing: steel production cost isn't just about iron ore prices. It's a layered equation involving coking coal, electricity, labor, emissions compliance, logistics, and technology choice. A…
Egg Powder Manufacturing Plant Setup Cost | Cost Involved, Machinery Cost and In …
IMARC Group's report titled "Egg Powder Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2024: Industry Trends, Plant Setup, Machinery, Raw Materials, Investment Opportunities, Cost and Revenue" provides a comprehensive guide for establishing an egg powder manufacturing plant. The report covers various aspects, ranging from a broad market overview to intricate details like unit operations, raw material and utility requirements, infrastructure necessities, machinery requirements, manpower needs, packaging and transportation requirements, and more.
In addition to…
Glucose Manufacturing Plant Cost Report 2024: Requirements and Cost Involved
IMARC Group's report titled "Glucose Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2024: Industry Trends, Plant Setup, Machinery, Raw Materials, Investment Opportunities, Cost and Revenue" provides a comprehensive guide for establishing a glucose manufacturing plant. The report covers various aspects, ranging from a broad market overview to intricate details like unit operations, raw material and utility requirements, infrastructure necessities, machinery requirements, manpower needs, packaging and transportation requirements, and more.
In addition to the operational…
Fatty Alcohol Production Cost Analysis: Plant Cost, Price Trends, Raw Materials …
Syndicated Analytics' latest report titled "Fatty Alcohol Production Cost Analysis 2023-2028: Capital Investment, Manufacturing Process, Operating Cost, Raw Materials, Industry Trends and Revenue Statistics" includes all the essential aspects that are required to understand and venture into the fatty alcohol industry. This report is based on the latest economic data, and it presents comprehensive and detailed insights regarding the primary process flow, raw material requirements, reactions involved, utility costs, operating costs, capital…
Corn Production Cost Analysis Report: Manufacturing Process, Raw Materials Requi …
The latest report titled "Corn Production Cost Report" by Procurement Resource, a global procurement research and consulting firm, provides an in-depth cost analysis of the production process of the Corn. Read More: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/corn
Report Features - Details
Product Name - Corn Production
Segments Covered
Manufacturing Process: Process Flow, Material Flow, Material Balance
Raw Material and Product/s Specifications: Raw Material Consumption, Product and Co-Product Generation, Capital Investment
Land and Site Cost: Offsites/Civil Works, Equipment Cost, Auxiliary Equipment…
Crude Oil Production Cost Analysis Report: Manufacturing Process, Raw Materials …
The latest report titled "Crude Oil Production Cost Report" by Procurement Resource, a global procurement research and consulting firm, provides an in-depth cost analysis of the production process of the Crude Oil. Read More: https://www.procurementresource.com/production-cost-report-store/crude-oil
Report Features - Details
Product Name - Crude Oil
Segments Covered
Manufacturing Process: Process Flow, Material Flow, Material Balance
Raw Material and Product/s Specifications: Raw Material Consumption, Product and Co-Product Generation, Capital Investment
Land and Site Cost: Offsites/Civil Works, Equipment Cost,…
